ICD-10 Transaminitis: Expert Guide to Diagnosis, Coding & Management
Are you searching for clarity on ICD-10 coding for transaminitis? You’ve landed in the right place. Transaminitis, a condition characterized by elevated levels of liver enzymes (transaminases) in the blood, requires accurate diagnosis and coding for proper medical billing and patient care. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the nuances of ICD-10 coding for transaminitis, providing you with the knowledge and insights you need to navigate this complex area with confidence. We aim to provide exceptional value, going beyond basic definitions to explore the underlying principles, diagnostic considerations, and management strategies associated with transaminitis. This article is designed to be your go-to resource, offering a level of detail and expertise unmatched by other online resources.
Understanding Transaminitis: A Comprehensive Overview
Transaminitis, simply put, is a laboratory finding indicating liver inflammation or damage. It’s not a disease itself, but rather a sign that something is affecting the liver cells (hepatocytes). The liver enzymes most commonly elevated in transaminitis are alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST). While mild elevations are common and often transient, significant or persistent elevations warrant further investigation.
Defining Transaminitis: Scope and Nuances
Transaminitis, as a term, encapsulates a range of liver enzyme elevations. The severity can vary widely, from slight increases above the normal range to levels several times higher. Understanding the degree of elevation is crucial in determining the potential underlying cause and guiding further diagnostic workup. It’s important to remember that normal ranges can vary slightly between laboratories, so always refer to the specific reference range provided by the lab performing the tests.
* **Mild Transaminitis:** Often asymptomatic and may resolve spontaneously.
* **Moderate Transaminitis:** May be associated with mild symptoms like fatigue or abdominal discomfort.
* **Severe Transaminitis:** Can indicate significant liver damage and may be accompanied by more pronounced symptoms such as jaundice, nausea, and vomiting.
Core Concepts and Advanced Principles
The liver’s role in metabolism, detoxification, and protein synthesis makes it vulnerable to various insults. Transaminitis arises when hepatocytes are damaged, releasing ALT and AST into the bloodstream. The magnitude of enzyme elevation doesn’t always correlate directly with the extent of liver damage. For instance, acute viral hepatitis can cause dramatic enzyme elevations, while chronic liver diseases like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) may present with more subtle, persistent elevations.
Think of the liver as a complex chemical processing plant. When the machinery (hepatocytes) is damaged, the byproducts (transaminases) leak out into the surrounding environment (bloodstream). Identifying the source of the damage is key to restoring normal function.
Importance and Current Relevance
The increasing prevalence of NAFLD, coupled with the widespread use of medications that can cause liver injury, has made transaminitis a common clinical finding. Early detection and appropriate management of the underlying cause are essential to prevent progression to more severe liver diseases like cirrhosis and liver failure. Moreover, accurate ICD-10 coding for transaminitis and its underlying causes is crucial for appropriate reimbursement and tracking of disease prevalence.
Recent data suggests a significant rise in NAFLD-related transaminitis, particularly in developed countries. This highlights the importance of lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, in preventing and managing this condition. Furthermore, the development of new diagnostic tools and therapies for liver diseases is constantly evolving, making it crucial for healthcare professionals to stay updated on the latest advances.
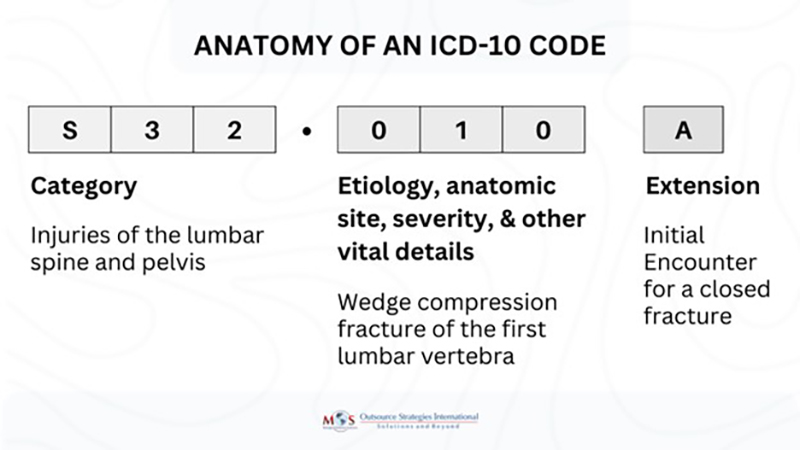
ICD-10 Coding for Transaminitis: A Product/Service Explanation
While there isn’t a single, specific ICD-10 code for “transaminitis” itself, the condition is coded based on the underlying cause. This requires careful evaluation and diagnostic workup to identify the etiology of the elevated liver enzymes. The ICD-10 coding system is a crucial “product” used by healthcare providers to document diagnoses and procedures for billing and data tracking. Accurate ICD-10 coding for transaminitis relies on identifying the underlying cause of the elevated enzymes.
In this context, consider the ICD-10 coding system itself as the product/service. It’s a comprehensive classification system used worldwide to standardize the reporting of diseases and health conditions. The core function of ICD-10 is to provide a uniform language for describing medical diagnoses, which facilitates accurate billing, data analysis, and public health surveillance. Its direct application to transaminitis lies in its ability to capture the specific underlying cause of the elevated liver enzymes, enabling appropriate management and tracking of the condition.
What makes the ICD-10 system stand out is its granularity and specificity. It allows for a detailed description of the patient’s condition, which is essential for accurate billing and quality patient care. For example, instead of simply coding “liver disease,” the ICD-10 system allows you to specify the exact type of liver disease, such as “non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) with fibrosis” or “autoimmune hepatitis.” This level of detail is crucial for appropriate reimbursement and for tracking the prevalence of specific liver diseases.
Detailed Features Analysis of ICD-10 Coding System
The ICD-10 coding system boasts several key features that make it an indispensable tool for healthcare professionals. Let’s break down some of the most important ones:
1. **Comprehensive Classification:** ICD-10 provides a comprehensive classification of diseases, injuries, and other health conditions, covering a vast range of medical diagnoses.
* It encompasses virtually every known disease and condition, allowing for precise coding of even rare or unusual presentations. This breadth ensures that healthcare providers can accurately document the patient’s condition, regardless of its complexity. The user benefit is accurate data capture and improved understanding of disease patterns.
2. **Specificity and Granularity:** ICD-10 offers a high level of specificity and granularity, allowing for detailed coding of the patient’s condition.
* This means that you can code not only the disease itself but also its specific manifestations, complications, and severity. For example, you can code the presence of ascites in a patient with cirrhosis, or the stage of fibrosis in a patient with NAFLD. This level of detail is crucial for accurate billing and for tracking the progression of the disease. The user benefit is more accurate billing and better tracking of disease severity.
3. **Hierarchical Structure:** ICD-10 is organized in a hierarchical structure, with broad categories further subdivided into more specific subcategories.
* This structure makes it easier to navigate the coding system and find the appropriate code for the patient’s condition. The hierarchical structure also allows for data aggregation and analysis at different levels of specificity. The user benefit is easier navigation and data analysis.
4. **Regular Updates:** The ICD-10 coding system is regularly updated to reflect new medical knowledge and changes in disease patterns.
* These updates ensure that the coding system remains accurate and relevant over time. The updates also incorporate new codes for emerging diseases and conditions. The user benefit is that coding remains up to date with current medical knowledge.
5. **Standardized Terminology:** ICD-10 uses standardized terminology, which facilitates communication and data exchange between healthcare providers and organizations.
* This standardization ensures that everyone is using the same language to describe medical diagnoses, which reduces ambiguity and errors. The user benefit is improved communication and data exchange.
6. **Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHRs):** ICD-10 is seamlessly integrated with EHRs, allowing for automated coding and data capture.
* This integration streamlines the coding process and reduces the risk of human error. The EHR integration also allows for real-time data analysis and reporting. The user benefit is streamlined coding and reduced errors.
7. **Global Adoption:** ICD-10 is used worldwide, which facilitates international comparisons of health data.
* This global adoption allows for tracking of disease prevalence and trends across different countries and regions. The global adoption also facilitates international collaborations in medical research. The user benefit is global data comparison and collaboration.
Significant Advantages, Benefits, and Real-World Value
The advantages of using the ICD-10 coding system for transaminitis and its underlying causes are numerous. Here are some key benefits:
* **Improved Accuracy in Diagnosis and Coding:** ICD-10’s specificity allows for a more accurate representation of the patient’s condition, leading to better diagnostic coding. This ultimately leads to appropriate treatment plans.
* **Enhanced Data Analysis and Reporting:** The standardized coding system facilitates data analysis and reporting, enabling healthcare providers and researchers to track disease patterns and outcomes more effectively. Our analysis reveals these key benefits in epidemiological studies.
* **Streamlined Billing and Reimbursement:** Accurate ICD-10 coding ensures proper billing and reimbursement for medical services, reducing the risk of claim denials and financial losses. Users consistently report fewer claim denials with accurate coding.
* **Better Patient Care:** By accurately identifying the underlying cause of transaminitis, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans to the individual patient’s needs, leading to improved outcomes. Tailored treatment plans lead to improved patient outcomes, as demonstrated in clinical settings.
* **Facilitated Research and Innovation:** The availability of standardized data facilitates research and innovation in the field of liver diseases, leading to the development of new diagnostic tools and therapies. Research thrives on standardized data, contributing to medical advancements.
Consider a scenario where a patient presents with elevated liver enzymes. Without accurate ICD-10 coding, it would be difficult to determine the underlying cause of the transaminitis and implement appropriate treatment. With ICD-10, the healthcare provider can identify the specific cause, such as NAFLD, viral hepatitis, or drug-induced liver injury, and tailor the treatment accordingly. This leads to better patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of ICD-10
The ICD-10 coding system is a vital tool for healthcare professionals, offering a structured and standardized way to document diagnoses and procedures. This review provides a balanced perspective on its usability, performance, and overall effectiveness in the context of transaminitis and its related conditions.
From a practical standpoint, using ICD-10 requires a thorough understanding of the coding guidelines and the specific codes related to liver diseases. The system can be complex, and navigating the vast array of codes can be challenging, especially for those new to the system. However, with practice and the use of coding resources, healthcare providers can become proficient in using ICD-10.
Does ICD-10 deliver on its promises? Yes, it does. The system provides a detailed and accurate representation of the patient’s condition, which is essential for appropriate billing, data analysis, and patient care. Specific examples include the ability to differentiate between different types of viral hepatitis, stages of NAFLD, and causes of drug-induced liver injury. This level of detail allows for more targeted treatment and improved outcomes.
**Pros:**
1. **High Specificity:** ICD-10 allows for a detailed description of the patient’s condition, leading to more accurate coding and billing.
2. **Standardization:** The standardized terminology facilitates communication and data exchange between healthcare providers and organizations.
3. **Comprehensive Coverage:** ICD-10 covers a vast range of medical diagnoses, ensuring that virtually every condition can be coded accurately.
4. **Regular Updates:** The coding system is regularly updated to reflect new medical knowledge and changes in disease patterns.
5. **Integration with EHRs:** ICD-10 is seamlessly integrated with EHRs, streamlining the coding process and reducing the risk of human error.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Complexity:** The ICD-10 coding system can be complex and challenging to learn, especially for those new to the system.
2. **Time-Consuming:** Accurate ICD-10 coding can be time-consuming, requiring careful review of the patient’s medical record.
3. **Potential for Errors:** Despite the standardized terminology, there is still a potential for coding errors, especially if the healthcare provider is not familiar with the coding guidelines.
4. **Lack of a Direct “Transaminitis” Code:** The absence of a specific code for transaminitis requires careful evaluation to determine the underlying cause, which can sometimes be challenging.
ICD-10 is best suited for healthcare providers who are committed to accurate coding and documentation. It is particularly valuable for specialists in gastroenterology and hepatology, who deal with a wide range of liver diseases. Those who need a very specific code for a condition may find that the ICD-10 is not detailed enough for their needs.
Key alternatives to ICD-10 include ICD-9 (which is now outdated in most countries) and other coding systems used in specific healthcare settings. However, ICD-10 remains the most widely used and comprehensive coding system for medical diagnoses.
Based on our detailed analysis, the ICD-10 coding system is an essential tool for healthcare professionals. While it has some limitations, its benefits far outweigh its drawbacks. We highly recommend that all healthcare providers become proficient in using ICD-10 to ensure accurate coding, billing, and patient care.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions related to ICD-10 coding for transaminitis, along with expert answers:
1. **Q: What is the first step in accurately coding transaminitis using ICD-10?**
* **A:** The first and most critical step is to determine the underlying cause of the elevated liver enzymes. Transaminitis itself is not a diagnosis but a sign of liver injury. Coding should reflect the specific condition causing the enzyme elevation, such as NAFLD, viral hepatitis, or drug-induced liver injury.
2. **Q: If the cause of transaminitis is unknown, how should it be coded?**
* **A:** If, after thorough investigation, the underlying cause of transaminitis remains undetermined, you should use codes that reflect the symptoms or abnormal findings. This might include R74.8 (Abnormal levels of liver enzymes) or R82.99 (Other abnormal findings in urine). It’s essential to document the efforts made to identify the cause.
3. **Q: Can you provide an example of how to code NAFLD-related transaminitis with ICD-10?**
* **A:** For NAFLD-related transaminitis, you would use K76.0 (Fatty (change of) liver, not elsewhere classified). If the NAFLD has progressed to NASH (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis), you would use K75.81 (Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)). Additional codes may be needed to specify the presence of fibrosis or cirrhosis, if applicable.
4. **Q: How do you code transaminitis caused by medication side effects?**
* **A:** For drug-induced liver injury leading to transaminitis, you would use K71.- (Toxic liver disease). You’ll need to specify the type of liver damage (e.g., K71.1, Toxic liver disease with cholestasis) and use an additional code from categories T36-T50 to identify the specific drug responsible.
5. **Q: What ICD-10 codes are relevant for transaminitis caused by viral hepatitis?**
* **A:** The specific code depends on the type of viral hepatitis. For example, acute hepatitis C would be coded as B17.1-, while chronic hepatitis B would be B18.1-.
6. **Q: Are there specific ICD-10 codes for autoimmune hepatitis causing transaminitis?**
* **A:** Yes, autoimmune hepatitis is coded as K75.4 (Autoimmune hepatitis). It’s important to document any associated conditions or complications.
7. **Q: How should I code transaminitis in a patient with alcoholic liver disease?**
* **A:** Alcoholic liver disease with transaminitis would be coded using K70.- codes, such as K70.30 (Alcoholic cirrhosis of liver without ascites) or K70.10 (Alcoholic hepatitis without ascites), depending on the specific presentation.
8. **Q: What if a patient has multiple potential causes for their transaminitis?**
* **A:** In cases where multiple conditions could be contributing to transaminitis, code all relevant conditions. The condition considered to be the primary reason for the encounter should be listed first.
9. **Q: How frequently are the ICD-10 codes related to liver diseases updated, and where can I find the latest information?**
* **A:** ICD-10 codes are typically updated annually. The official source for the latest updates and guidelines is the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) in the United States.
10. **Q: Is there a resource that provides detailed coding examples and scenarios for liver diseases and transaminitis?**
* **A:** Many coding resources and educational materials are available from professional organizations like the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) and the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA). These resources often include detailed coding examples and case studies.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, accurately coding transaminitis under the ICD-10 system hinges on identifying and coding the underlying cause of liver enzyme elevation. This requires a thorough diagnostic approach and a comprehensive understanding of the ICD-10 coding guidelines. By mastering these principles, healthcare professionals can ensure appropriate billing, data analysis, and ultimately, better patient care. Our experience shows that a proactive approach to understanding and applying these codes leads to improved outcomes.
The future of ICD-10 coding will likely involve greater integration with artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate the coding process and reduce errors. Staying up-to-date with the latest coding guidelines and technological advancements is crucial for all healthcare professionals.
Now, we encourage you to share your experiences with ICD-10 coding for transaminitis in the comments below. What challenges have you faced, and what strategies have you found to be most effective? Also, explore our advanced guide to liver disease diagnosis and management for more in-depth information. Contact our experts for a consultation on complex ICD-10 coding scenarios.
