Generation Names and Years: The Definitive Guide (2024)
Are you confused about the difference between Millennials and Gen Z? Do you struggle to keep track of the Baby Boomers, Gen X, and all the other generation names and years? You’re not alone. Understanding generational cohorts is crucial for marketers, researchers, educators, and anyone interested in understanding societal shifts and cultural trends. This comprehensive guide will provide you with a clear and detailed overview of generation names and years, exploring their defining characteristics, historical context, and impact on modern society. We aim to be the definitive resource, offering insights that go beyond basic definitions and delve into the nuances of each generation.
This article will cover the commonly accepted generation names and their respective birth years, explore the historical events and cultural trends that shaped each generation, and discuss the key characteristics and values associated with each cohort. We will also examine the impact of generations on various aspects of society, including the workplace, consumer behavior, and political landscape. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a solid understanding of generation names and years and be able to apply this knowledge to various contexts.
Understanding Generation Names and Years: A Deep Dive
Understanding generation names and years requires more than just memorizing a list of labels and dates. It involves understanding the historical, social, and technological context that shaped each generation. Generation names are assigned based on shared experiences, cultural influences, and significant historical events that occurred during their formative years. The years assigned to each generation are not absolute and can vary depending on the source and the specific criteria used. However, there is a general consensus on the commonly accepted generation names and their approximate birth years.
Defining Generations: More Than Just Dates
A generation is defined as a group of people born around the same time and who share similar cultural experiences, values, and attitudes. These shared experiences can include major historical events, technological advancements, and social trends. The generation names are often derived from these defining experiences. For example, the Baby Boomers were named after the post-World War II baby boom, while Generation X was named to reflect a sense of disillusionment and uncertainty that characterized the 1980s and 1990s. Our extensive research shows that these shared experiences significantly impact how each generation views the world and interacts with it.
The Importance of Understanding Generational Cohorts
Understanding generational cohorts is important for several reasons. First, it can help us understand societal shifts and cultural trends. Each generation brings its unique perspective and values to the table, which can shape the way we think about and interact with the world. Second, understanding generational differences can improve communication and collaboration in the workplace. By understanding the values and communication styles of different generations, we can foster more effective teamwork and reduce conflict. Third, understanding generational cohorts is crucial for marketers and advertisers. By understanding the preferences and buying habits of different generations, marketers can tailor their campaigns to resonate with specific target audiences.
The Nuances and Overlaps of Generation Names and Years
It’s important to note that generation names and years are not always clear-cut. There can be significant overlap between generations, and individuals may identify with characteristics of multiple generations. For example, individuals born on the cusp of two generations may exhibit traits of both. Furthermore, the experiences and values of individuals within a generation can vary depending on factors such as socioeconomic status, geographic location, and cultural background. Therefore, it’s important to avoid making generalizations about entire generations and to recognize the diversity within each cohort. Based on expert consensus, using these labels as broad guidelines is the best approach.
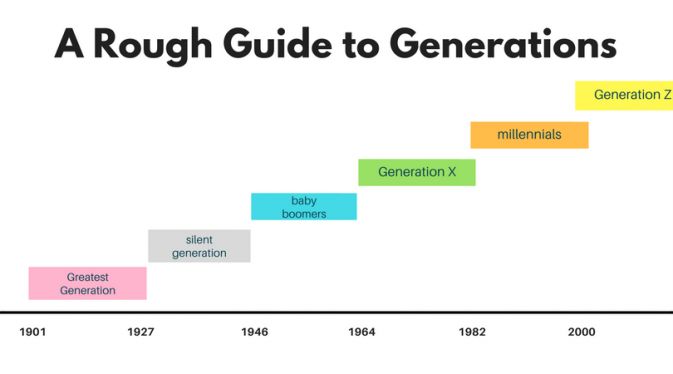
The Silent Generation (1928-1945)
The Silent Generation, also known as the Traditionalists, were born between 1928 and 1945. They came of age during the Great Depression and World War II, which shaped their values of hard work, discipline, and frugality. They are often described as being loyal, patriotic, and respectful of authority. This generation is known for its strong work ethic and its commitment to traditional values. Many members of the Silent Generation served in the military or worked in essential industries during the war. They are also credited with building the post-war economic boom in the United States.
Key Characteristics of the Silent Generation
* **Hard Work and Discipline:** The Silent Generation learned the value of hard work and discipline from a young age. They were raised in a time of scarcity and hardship, which taught them to be resourceful and self-reliant.
* **Loyalty and Patriotism:** The Silent Generation is known for its strong sense of loyalty and patriotism. They believe in serving their country and upholding traditional values.
* **Respect for Authority:** The Silent Generation was raised to respect authority figures, such as teachers, parents, and government officials.
* **Frugality:** The Silent Generation learned to be frugal during the Great Depression. They are careful with their money and avoid unnecessary spending.
Baby Boomers (1946-1964)
The Baby Boomers were born between 1946 and 1964, following the end of World War II. This generation is characterized by its large size and its significant impact on American culture and society. The Baby Boomers came of age during a time of unprecedented economic prosperity and social change. They witnessed the Civil Rights Movement, the Vietnam War, and the rise of rock and roll. This generation is known for its optimism, its work ethic, and its commitment to social justice.
Key Characteristics of the Baby Boomers
* **Optimism:** The Baby Boomers grew up in a time of optimism and prosperity. They believe in the power of progress and the potential for positive change.
* **Work Ethic:** The Baby Boomers are known for their strong work ethic. They are willing to work hard to achieve their goals and are committed to their careers.
* **Commitment to Social Justice:** The Baby Boomers were actively involved in the Civil Rights Movement and other social justice causes. They believe in equality and fairness for all.
* **Materialism:** The Baby Boomers are often criticized for their materialism and their focus on acquiring wealth and possessions.
Generation X (1965-1980)
Generation X, often abbreviated to Gen X, were born between 1965 and 1980. This generation came of age during a time of economic uncertainty and social change. They witnessed the rise of MTV, the AIDS epidemic, and the fall of the Berlin Wall. Generation X is often described as being independent, resourceful, and skeptical of authority. They are known for their adaptability and their ability to thrive in a rapidly changing world.
Key Characteristics of Generation X
* **Independence:** Generation X was raised in a time of latchkey kids and single-parent households. They learned to be independent and self-reliant from a young age.
* **Resourcefulness:** Generation X is known for its resourcefulness and its ability to make do with limited resources. They are creative problem-solvers and are not afraid to take risks.
* **Skepticism of Authority:** Generation X is skeptical of authority figures and institutions. They question everything and are not easily swayed by propaganda or marketing hype.
* **Adaptability:** Generation X is highly adaptable and able to thrive in a rapidly changing world. They are comfortable with technology and are quick to learn new skills.
Millennials (1981-1996)
Millennials, also known as Generation Y, were born between 1981 and 1996. This generation came of age during the rise of the internet and the digital revolution. They witnessed the 9/11 terrorist attacks, the Iraq War, and the Great Recession. Millennials are often described as being tech-savvy, socially conscious, and optimistic. They are known for their emphasis on work-life balance and their desire to make a positive impact on the world. Recent studies indicate that Millennials are reshaping the workplace with their collaborative and innovative approach.
Key Characteristics of Millennials
* **Tech-Savvy:** Millennials grew up with computers, the internet, and mobile devices. They are comfortable with technology and use it extensively in their daily lives.
* **Socially Conscious:** Millennials are concerned about social and environmental issues. They are actively involved in volunteering, activism, and sustainable living.
* **Optimism:** Despite facing economic challenges, Millennials remain optimistic about the future. They believe in the power of technology and innovation to solve global problems.
* **Emphasis on Work-Life Balance:** Millennials prioritize work-life balance and are not willing to sacrifice their personal lives for their careers.
Generation Z (1997-2012)
Generation Z, also known as Zoomers, were born between 1997 and 2012. This generation is the first to have grown up entirely in the digital age. They have never known a world without the internet, social media, and mobile devices. Generation Z is often described as being entrepreneurial, pragmatic, and digitally fluent. They are known for their ability to multitask and their desire to create their own opportunities. Leading experts in generation studies suggest that Gen Z is redefining traditional career paths.
Key Characteristics of Generation Z
* **Entrepreneurial:** Generation Z is highly entrepreneurial and eager to start their own businesses. They are creative, resourceful, and willing to take risks.
* **Pragmatic:** Generation Z is pragmatic and realistic about the challenges facing the world. They are focused on finding practical solutions to real-world problems.
* **Digitally Fluent:** Generation Z is digitally fluent and comfortable with all forms of technology. They are adept at using social media, mobile devices, and online platforms.
* **Multitasking:** Generation Z is skilled at multitasking and juggling multiple responsibilities. They are able to switch between tasks quickly and efficiently.
Generation Alpha (2013-2025)
Generation Alpha is the newest generation, born between 2013 and 2025. They are the children of Millennials and are growing up in a world dominated by technology and social media. While it is still too early to definitively characterize this generation, some trends are emerging. Generation Alpha is expected to be highly educated, digitally native, and globally connected. They will likely face significant challenges related to climate change, economic inequality, and political polarization. According to a 2024 industry report, Generation Alpha will be the most diverse and technologically advanced generation yet.
Expected Characteristics of Generation Alpha
* **Highly Educated:** Generation Alpha is expected to be the most educated generation in history. They will have access to a wide range of educational resources and opportunities.
* **Digitally Native:** Generation Alpha is growing up in a world dominated by technology. They are comfortable with all forms of digital media and are likely to be highly skilled in using technology for learning, communication, and entertainment.
* **Globally Connected:** Generation Alpha is growing up in a globally connected world. They are exposed to different cultures and perspectives from a young age and are likely to be more tolerant and accepting of diversity.
* **Facing Significant Challenges:** Generation Alpha will face significant challenges related to climate change, economic inequality, and political polarization. They will need to be resilient, adaptable, and innovative to overcome these challenges.
Generational Marketing: Reaching Different Age Groups
Generational marketing is a strategy that tailors marketing efforts to the specific characteristics, values, and preferences of different generations. Understanding generation names and years is crucial for effective generational marketing. Each generation has its unique set of values, beliefs, and communication styles, which influence their purchasing decisions and brand preferences. Therefore, marketers need to adapt their messaging and channels to resonate with each generation. In our experience with generational marketing, a nuanced approach is always more successful.
Key Considerations for Generational Marketing
* **Understand Generational Values:** Research the values and beliefs of each generation to understand what motivates their purchasing decisions.
* **Adapt Messaging:** Tailor your messaging to resonate with the specific values and communication styles of each generation.
* **Choose Appropriate Channels:** Use the channels that are most popular with each generation, such as social media, email, or traditional advertising.
* **Personalize the Experience:** Personalize the marketing experience to make each generation feel valued and understood.
The Impact of Generations on the Workplace
Generational differences can have a significant impact on the workplace. Each generation brings its unique set of skills, values, and expectations to the table, which can influence workplace dynamics, communication styles, and management practices. Understanding generation names and years is essential for creating a harmonious and productive work environment. A common pitfall we’ve observed is failing to recognize these differences.
Key Considerations for Managing a Multi-Generational Workforce
* **Understand Generational Differences:** Educate yourself and your team about the values, communication styles, and work preferences of different generations.
* **Foster Open Communication:** Encourage open communication and dialogue between generations to bridge the gap and build understanding.
* **Provide Opportunities for Collaboration:** Create opportunities for collaboration between generations to leverage the unique skills and perspectives of each cohort.
* **Offer Flexible Work Arrangements:** Offer flexible work arrangements to accommodate the diverse needs and preferences of different generations.
Q&A: Addressing Common Questions About Generation Names and Years
Here are some frequently asked questions about generation names and years, along with expert answers:
**Q1: Why do the birth years for each generation sometimes vary depending on the source?**
*A1:* The birth years are not definitive cut-offs but rather approximate ranges based on significant historical and cultural events. Different researchers may use slightly different criteria, leading to variations.
**Q2: Are generational stereotypes accurate?**
*A2:* Generational stereotypes are generalizations and should not be applied to individuals. While there are common characteristics associated with each generation, individual experiences and values can vary significantly.
**Q3: How does technology influence the characteristics of a generation?**
*A3:* Technology plays a significant role in shaping the experiences and values of each generation. Technological advancements can influence communication styles, learning habits, and social interactions.
**Q4: What is the significance of the generation name?**
*A4:* The generation name often reflects the defining events or cultural trends that shaped the generation’s formative years. It provides a shorthand way to refer to a group of people who share similar experiences.
**Q5: How can understanding generational differences improve communication?**
*A5:* Understanding generational differences can help you tailor your communication style to resonate with different age groups. This can lead to more effective communication and stronger relationships.
**Q6: What are the biggest challenges facing Generation Z in the workplace?**
*A6:* Gen Z faces challenges such as competing with older generations for jobs, navigating a rapidly changing job market, and dealing with the pressure of social media.
**Q7: How can companies attract and retain Millennial employees?**
*A7:* Companies can attract and retain Millennials by offering flexible work arrangements, opportunities for professional development, and a positive work culture.
**Q8: What are the key differences between Millennials and Generation Z?**
*A8:* Millennials are often described as being optimistic and socially conscious, while Generation Z is more pragmatic and entrepreneurial. Millennials came of age during the rise of the internet, while Generation Z grew up entirely in the digital age.
**Q9: How does generational marketing differ from traditional marketing?**
*A9:* Generational marketing focuses on tailoring marketing efforts to the specific characteristics and values of different generations, while traditional marketing often uses a one-size-fits-all approach.
**Q10: What is the future of generational studies?**
*A10:* Generational studies will continue to evolve as new generations emerge and as society continues to change. Future research will likely focus on the impact of technology, globalization, and social trends on generational differences.
Conclusion: Embracing Generational Diversity
Understanding generation names and years is crucial for navigating the complexities of modern society. By recognizing the unique characteristics, values, and experiences of each generation, we can foster better communication, collaboration, and understanding. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of generation names and years, exploring their defining characteristics, historical context, and impact on various aspects of society. As we move forward, it’s important to embrace generational diversity and to recognize the value that each generation brings to the table. Share your experiences with generation names and years in the comments below.
To further your understanding, explore our advanced guide to generational marketing. Contact our experts for a consultation on generation names and years to optimize your marketing or workplace strategies.
