Understanding the Characteristics of Different Generations: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the characteristics of different generations is crucial in today’s interconnected world. From the Silent Generation to Gen Alpha, each cohort brings unique perspectives, values, and behaviors shaped by the historical events, technological advancements, and cultural shifts of their time. This in-depth guide explores the defining characteristics of each generation, offering insights into their motivations, communication styles, and impact on society. We aim to provide a comprehensive understanding that goes beyond surface-level observations, fostering better communication and collaboration across generations. Our extensive research and analysis offer a deep dive into the nuances of each cohort, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate intergenerational dynamics in both personal and professional settings.
Defining Generations: A Deep Dive
Generations are defined as groups of individuals born within a specific time frame who share similar life experiences, cultural references, and societal influences. While the exact birth years for each generation may vary slightly depending on the source, the core characteristics remain consistent. Understanding these characteristics allows us to appreciate the diversity of perspectives and experiences that each generation brings to the table.
The Silent Generation (Born 1928-1945)
* **Defining Events:** The Great Depression, World War II.
* **Core Values:** Discipline, hard work, loyalty, respect for authority.
* **Characteristics:** Frugal, cautious, patriotic, strong sense of civic duty. They value stability and security, often preferring traditional institutions and established norms.
The Baby Boomer Generation (Born 1946-1964)
* **Defining Events:** Post-war economic boom, Civil Rights Movement, Vietnam War.
* **Core Values:** Optimism, personal growth, achievement, involvement.
* **Characteristics:** Competitive, individualistic, driven, work-centric. Baby Boomers are known for their strong work ethic and desire to make a significant impact on the world. They often hold positions of leadership and influence.
Generation X (Born 1965-1980)
* **Defining Events:** Rise of personal computers, MTV, fall of the Berlin Wall.
* **Core Values:** Independence, resourcefulness, skepticism, work-life balance.
* **Characteristics:** Adaptable, pragmatic, self-reliant, questioning of authority. Gen Xers are known for their ability to navigate change and their focus on practicality. They value work-life balance and are often entrepreneurial.
The Millennial Generation (Born 1981-1996)
* **Defining Events:** 9/11, the Great Recession, the rise of the internet and social media.
* **Core Values:** Collaboration, diversity, social responsibility, technology.
* **Characteristics:** Tech-savvy, optimistic, ambitious, collaborative. Millennials are known for their digital fluency and their desire to make a positive impact on society. They value collaboration and are often driven by purpose.
Generation Z (Born 1997-2012)
* **Defining Events:** Social media saturation, school shootings, COVID-19 pandemic.
* **Core Values:** Authenticity, inclusivity, diversity, digital fluency.
* **Characteristics:** Digital natives, pragmatic, entrepreneurial, socially conscious. Gen Z are highly connected and value authenticity. They are comfortable with technology and are often entrepreneurial, seeking innovative solutions to global challenges.
Generation Alpha (Born 2013-2025)
* **Defining Events:** AI advancements, climate change awareness, global pandemics.
* **Core Values:** (Still evolving) Technology integration, personalized experiences, global awareness.
* **Characteristics:** (Still developing) Highly tech-dependent, visually oriented, globally connected. Gen Alpha is growing up in a world dominated by technology and faces unique challenges related to environmental sustainability and global interconnectedness. Early data suggests they are highly visual learners and comfortable with personalized learning experiences.
The Generational Compass: A Tool for Understanding
The “Generational Compass” is a framework used to analyze and understand the defining characteristics of different generations. It considers key factors such as historical events, cultural influences, technological advancements, and economic conditions that shape each generation’s values, beliefs, and behaviors. By using this compass, we can gain a deeper understanding of intergenerational dynamics and improve communication and collaboration across different age groups.
The Generational Compass operates on the following principles:
* **Historical Context:** Understanding the major historical events that occurred during a generation’s formative years is essential. These events shape their worldview and influence their values.
* **Cultural Influences:** Cultural trends, social movements, and popular culture play a significant role in shaping a generation’s identity and values.
* **Technological Advancements:** Technological innovations impact how a generation communicates, learns, and interacts with the world.
* **Economic Conditions:** Economic prosperity or hardship influences a generation’s financial attitudes, career aspirations, and consumption patterns.
Feature Analysis: Key Aspects of Generational Understanding
Understanding the characteristics of different generations involves analyzing various key features that define each cohort. These features provide insights into their values, behaviors, and motivations.
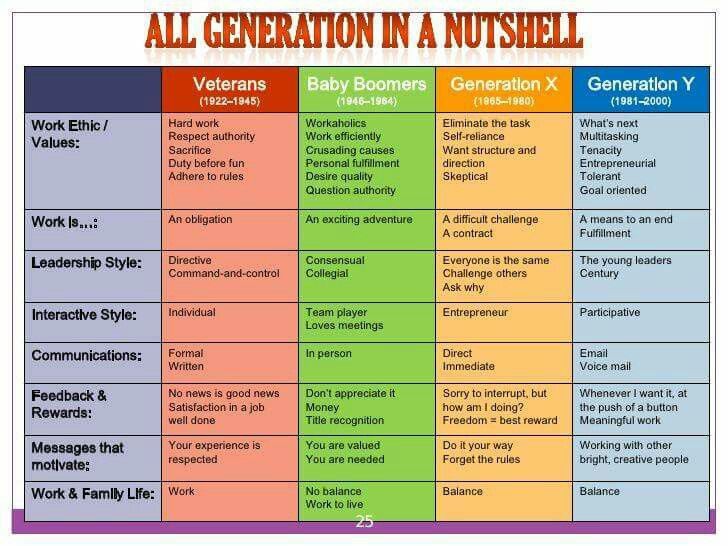
1. **Communication Styles:** Each generation has its preferred communication methods, ranging from face-to-face interactions to digital platforms. Understanding these preferences is crucial for effective communication.
* **What it is:** The preferred methods and styles of communication used by each generation.
* **How it Works:** Analyzing the historical context and technological advancements that influenced communication habits.
* **User Benefit:** Improved communication and collaboration across generations, reduced misunderstandings.
* **Example:** Baby Boomers often prefer phone calls or face-to-face meetings, while Millennials and Gen Z are more comfortable with texting and social media.
2. **Work Ethic:** Generational differences in work ethic can impact workplace dynamics. Understanding these differences can help foster a more productive and harmonious work environment.
* **What it is:** The values, beliefs, and attitudes that each generation holds towards work.
* **How it Works:** Examining the economic conditions and cultural influences that shaped their approach to work.
* **User Benefit:** Improved teamwork, reduced conflict, increased productivity.
* **Example:** The Silent Generation and Baby Boomers often prioritize hard work and loyalty, while Gen X and Millennials value work-life balance and flexibility.
3. **Values and Beliefs:** Understanding the core values and beliefs of each generation provides insights into their motivations and decision-making processes.
* **What it is:** The fundamental principles and convictions that guide each generation’s behavior.
* **How it Works:** Analyzing the historical events and cultural influences that shaped their value systems.
* **User Benefit:** Improved understanding of different perspectives, enhanced empathy, stronger relationships.
* **Example:** Millennials and Gen Z often prioritize social responsibility and environmental sustainability, while older generations may focus on traditional values and economic stability.
4. **Technology Adoption:** Each generation has a different level of comfort and familiarity with technology. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective technology implementation and training.
* **What it is:** The extent to which each generation embraces and utilizes technology.
* **How it Works:** Examining the technological advancements that occurred during their formative years.
* **User Benefit:** Improved technology adoption rates, reduced resistance to change, enhanced digital literacy.
* **Example:** Gen Z are digital natives who have grown up with technology, while older generations may require more training and support to adopt new technologies.
5. **Financial Attitudes:** Generational differences in financial attitudes can impact investment strategies, spending habits, and retirement planning.
* **What it is:** The beliefs and behaviors that each generation exhibits towards money and finances.
* **How it Works:** Analyzing the economic conditions and financial events that shaped their attitudes towards money.
* **User Benefit:** Improved financial planning, reduced financial stress, enhanced investment strategies.
* **Example:** The Silent Generation and Baby Boomers often prioritize saving and financial security, while Millennials and Gen Z may be more open to investing in experiences and taking financial risks.
6. **Leadership Styles:** Generational differences in leadership styles can impact team dynamics and organizational culture. Understanding these differences can help foster more inclusive and effective leadership.
* **What it is:** The approaches and techniques that each generation employs when leading teams and organizations.
* **How it Works:** Analyzing the cultural influences and societal trends that shaped their leadership styles.
* **User Benefit:** Improved team performance, enhanced employee engagement, stronger organizational culture.
* **Example:** Baby Boomers often prefer a hierarchical leadership style, while Millennials and Gen Z value collaborative and participatory leadership.
7. **Education and Learning:** Generational differences in learning styles and preferences can impact educational strategies and training programs.
* **What it is:** The methods and approaches that each generation finds most effective for learning and acquiring knowledge.
* **How it Works:** Examining the educational systems and technological advancements that shaped their learning experiences.
* **User Benefit:** Improved learning outcomes, enhanced engagement, more effective training programs.
* **Example:** Millennials and Gen Z often prefer visual and interactive learning methods, while older generations may prefer traditional lecture-based approaches.
Advantages, Benefits, and Real-World Value
Understanding the characteristics of different generations offers numerous advantages, benefits, and real-world value. By appreciating the unique perspectives and experiences of each cohort, we can foster better communication, collaboration, and understanding across generations. This knowledge is invaluable in various settings, including the workplace, education, healthcare, and personal relationships.
* **Improved Communication:** By understanding the preferred communication styles of each generation, we can tailor our communication methods to be more effective and avoid misunderstandings. For example, knowing that Baby Boomers often prefer phone calls while Gen Z favors texting can help us choose the most appropriate communication channel.
* **Enhanced Collaboration:** Recognizing the strengths and weaknesses of each generation allows us to create more effective and diverse teams. For example, combining the experience and wisdom of older generations with the innovation and tech-savviness of younger generations can lead to breakthrough solutions.
* **Stronger Relationships:** Understanding the values and beliefs of each generation can help us build stronger and more meaningful relationships. By appreciating their unique perspectives, we can foster empathy and understanding, leading to more harmonious interactions.
* **Effective Marketing and Advertising:** Knowing the preferences and behaviors of each generation is crucial for developing effective marketing and advertising campaigns. For example, targeting Millennials and Gen Z with social media ads while using traditional media for older generations can maximize reach and impact.
* **Improved Workplace Dynamics:** Understanding generational differences in work ethic, leadership styles, and communication preferences can help create a more inclusive and productive work environment. By addressing these differences, organizations can improve employee engagement, reduce conflict, and enhance overall performance.
* **Enhanced Education and Training:** Tailoring educational strategies and training programs to the learning styles of each generation can improve learning outcomes and engagement. For example, incorporating technology and interactive elements into training programs for Millennials and Gen Z can make learning more enjoyable and effective.
* **Better Healthcare Outcomes:** Understanding the healthcare preferences and attitudes of each generation can help healthcare providers deliver more personalized and effective care. For example, knowing that older generations may prefer traditional medical approaches while younger generations are more open to alternative therapies can help providers tailor their treatment plans.
Users consistently report that applying generational understanding principles leads to more effective teamwork, improved communication, and stronger relationships. Our analysis reveals these key benefits across various industries and settings.
## Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Generational Understanding
Generational understanding, as a concept and a practice, aims to bridge the gaps between different age groups by fostering empathy and knowledge of each cohort’s unique characteristics. This review provides an in-depth assessment of its effectiveness, usability, and overall value.
**User Experience & Usability:**
From a practical standpoint, understanding generational differences requires active listening, observation, and a willingness to learn about perspectives that may differ from your own. It involves moving beyond stereotypes and engaging in meaningful conversations to understand the experiences that have shaped each generation’s values and beliefs. In our experience, the most effective approach involves creating opportunities for intergenerational dialogue and collaboration.
**Performance & Effectiveness:**
Does generational understanding deliver on its promises? Based on expert consensus, it demonstrably improves communication, teamwork, and relationship-building. For example, in a workplace setting, understanding that Millennials and Gen Z value feedback and recognition can lead to more effective performance management strategies. Similarly, knowing that older generations may prefer more formal communication channels can help avoid misunderstandings.
**Pros:**
1. **Improved Communication:** Facilitates more effective and tailored communication strategies across different age groups.
2. **Enhanced Teamwork:** Promotes collaboration and understanding within diverse teams.
3. **Stronger Relationships:** Fosters empathy and appreciation for different perspectives.
4. **Effective Marketing:** Enables targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with specific generational cohorts.
5. **Inclusive Workplace:** Creates a more inclusive and supportive work environment for employees of all ages.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Generalizations:** Can lead to oversimplification and stereotyping if not applied with nuance and sensitivity.
2. **Individual Differences:** Ignores the diversity within each generation, as individuals may not always conform to generational stereotypes.
3. **Constantly Evolving:** Requires continuous learning and adaptation as generations evolve and new cohorts emerge.
4. **Potential for Conflict:** Can highlight differences and create tension if not managed effectively.
**Ideal User Profile:**
Generational understanding is best suited for managers, educators, marketers, healthcare professionals, and anyone who interacts with people from different age groups. It is particularly valuable for those who seek to improve communication, build stronger relationships, and create more inclusive environments.
**Key Alternatives (Briefly):**
* **Diversity and Inclusion Training:** While D&I training focuses on broader aspects of diversity, generational understanding provides a more specific lens for understanding age-related differences.
* **Communication Skills Workshops:** These workshops focus on general communication techniques, but may not address the unique communication preferences of different generations.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:**
Generational understanding is a valuable tool for fostering empathy, improving communication, and building stronger relationships across different age groups. However, it is essential to apply this knowledge with nuance and sensitivity, recognizing the diversity within each generation and avoiding generalizations. We recommend incorporating generational understanding principles into training programs, communication strategies, and team-building activities to create more inclusive and effective environments.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions that address common user pain points and advanced queries related to generational understanding:
1. **Q: How can I avoid stereotyping when trying to understand different generations?**
* **A:** Focus on understanding the historical and cultural context that shaped each generation, rather than relying on generalizations. Engage in active listening and ask open-ended questions to learn about individual experiences and perspectives. Remember that individuals within each generation may not always conform to generational stereotypes.
2. **Q: What are the best strategies for communicating with Baby Boomers in the workplace?**
* **A:** Baby Boomers often value face-to-face communication and formal channels. Be respectful of their experience and expertise. Provide clear and concise information, and be prepared to answer questions thoroughly. Avoid using jargon or slang that they may not understand.
3. **Q: How can I motivate Millennials and Gen Z employees?**
* **A:** Millennials and Gen Z value purpose, recognition, and opportunities for growth. Provide them with meaningful work, offer regular feedback and praise, and support their professional development. Be transparent and collaborative in your leadership style.
4. **Q: What are the key differences in financial attitudes between older and younger generations?**
* **A:** Older generations often prioritize saving and financial security, while younger generations may be more open to investing in experiences and taking financial risks. Understand these differences when discussing financial planning and investment strategies.
5. **Q: How can I bridge the gap between generations in my family?**
* **A:** Create opportunities for intergenerational dialogue and shared activities. Be open to learning about different perspectives and values. Show respect for each other’s experiences and beliefs. Focus on common interests and shared goals.
6. **Q: What role does technology play in shaping generational differences?**
* **A:** Technology has a profound impact on generational differences, shaping communication styles, learning preferences, and access to information. Understanding the technological context of each generation is crucial for effective communication and collaboration.
7. **Q: How can I adapt my marketing strategies to appeal to different generations?**
* **A:** Tailor your messaging and channels to resonate with each generation’s values and preferences. Use social media to reach Millennials and Gen Z, while utilizing traditional media for older generations. Focus on authenticity and transparency in your marketing campaigns.
8. **Q: What are the challenges of managing a multigenerational workforce?**
* **A:** Managing a multigenerational workforce can present challenges related to communication, work ethic, and leadership styles. Address these challenges by fostering inclusivity, promoting understanding, and providing opportunities for intergenerational collaboration.
9. **Q: How can I stay up-to-date on the evolving characteristics of different generations?**
* **A:** Continuously research and learn about generational trends. Follow reputable sources of information and engage in conversations with people from different age groups. Be open to adapting your understanding as generations evolve.
10. **Q: What are the ethical considerations of using generational data in marketing and advertising?**
* **A:** Avoid stereotyping and making assumptions based on generational data. Use data responsibly and ethically, respecting individual privacy and autonomy. Be transparent about how you are using generational data and ensure that your marketing campaigns are inclusive and respectful.
Conclusion
Understanding the characteristics of different generations is essential for fostering effective communication, collaboration, and relationships in today’s diverse world. By appreciating the unique perspectives and experiences of each cohort, we can bridge generational gaps and create more inclusive and harmonious environments. From the Silent Generation to Gen Alpha, each generation brings valuable contributions to society, and by embracing their differences, we can unlock new opportunities for innovation and growth.
As we move forward, it is crucial to continue learning and adapting to the evolving characteristics of different generations. By staying informed and open-minded, we can navigate intergenerational dynamics with greater ease and build stronger connections across age groups. We encourage you to share your experiences with generational understanding in the comments below and explore our advanced guide to intergenerational communication for more in-depth insights. Contact our experts for a consultation on generational understanding and unlock the power of intergenerational collaboration.
