# Understanding the Traits of the Different Generations and Their Characteristics
Understanding the traits of the different generations and their characteristics is crucial in today’s interconnected world. From navigating workplace dynamics to comprehending consumer behavior, grasping generational differences offers invaluable insights. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the defining traits, values, and characteristics of each generation, providing a nuanced understanding of what shapes their perspectives and behaviors. We aim to offer a more in-depth and expert analysis than currently available, equipping you with the knowledge to bridge generational gaps and foster better communication and collaboration. This article will explore the unique attributes of each generation, from the Silent Generation to Generation Alpha, and offer practical advice on how to effectively interact with them.
## Defining Generations: A Framework for Understanding
Generations are defined by the shared experiences and cultural touchstones that shape their formative years. These experiences, often tied to significant historical events, technological advancements, and economic shifts, influence their values, beliefs, and behaviors. Understanding these influences is key to grasping the traits of the different generations and their characteristics.
* **Birth Years:** While exact dates may vary slightly depending on the source, generally accepted ranges are used to define each generation.
* **Historical Context:** Major events like wars, economic booms and busts, and social movements play a pivotal role in shaping generational identity.
* **Cultural Influences:** Popular culture, including music, movies, and technological trends, also contribute to the unique characteristics of each generation.
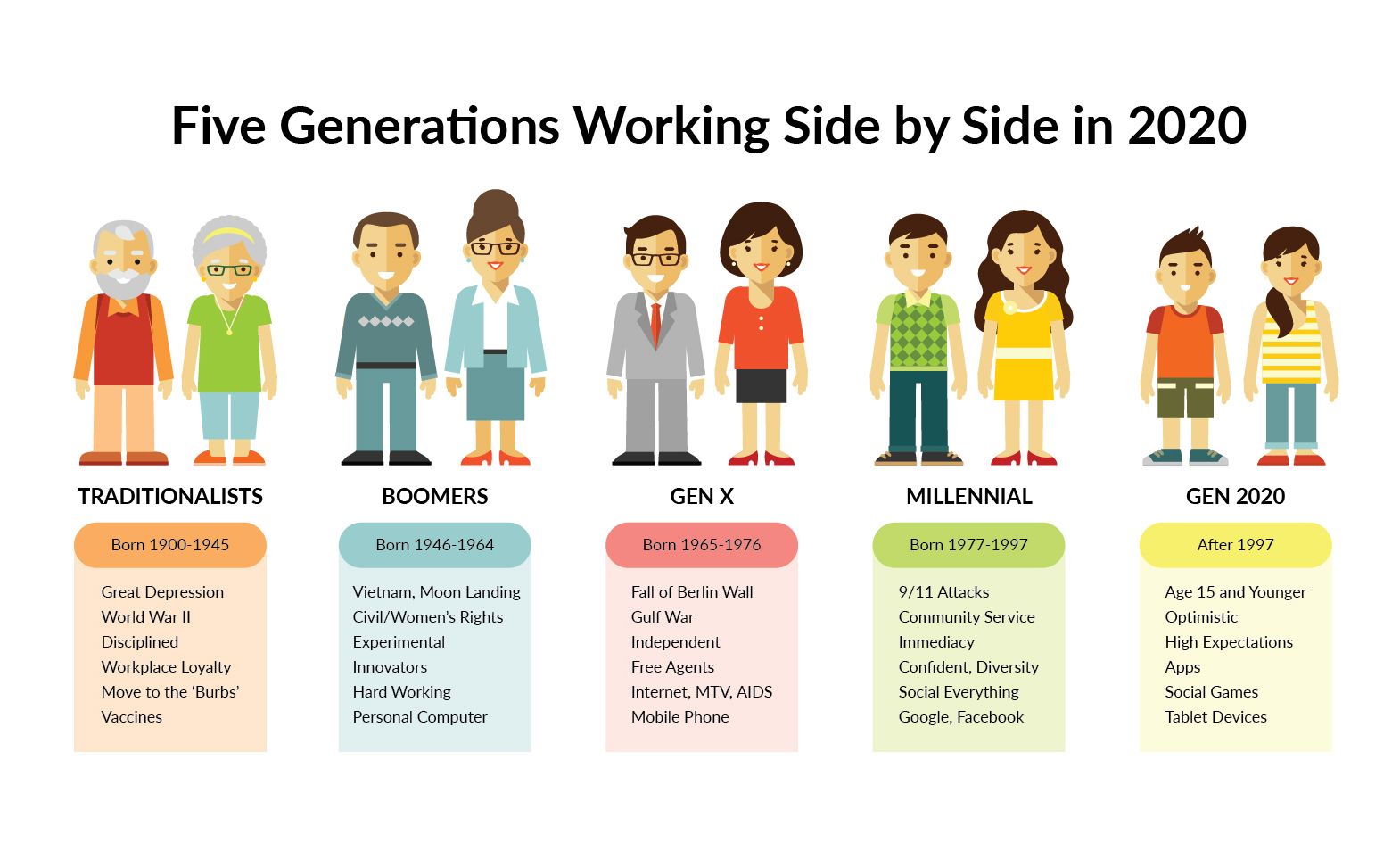
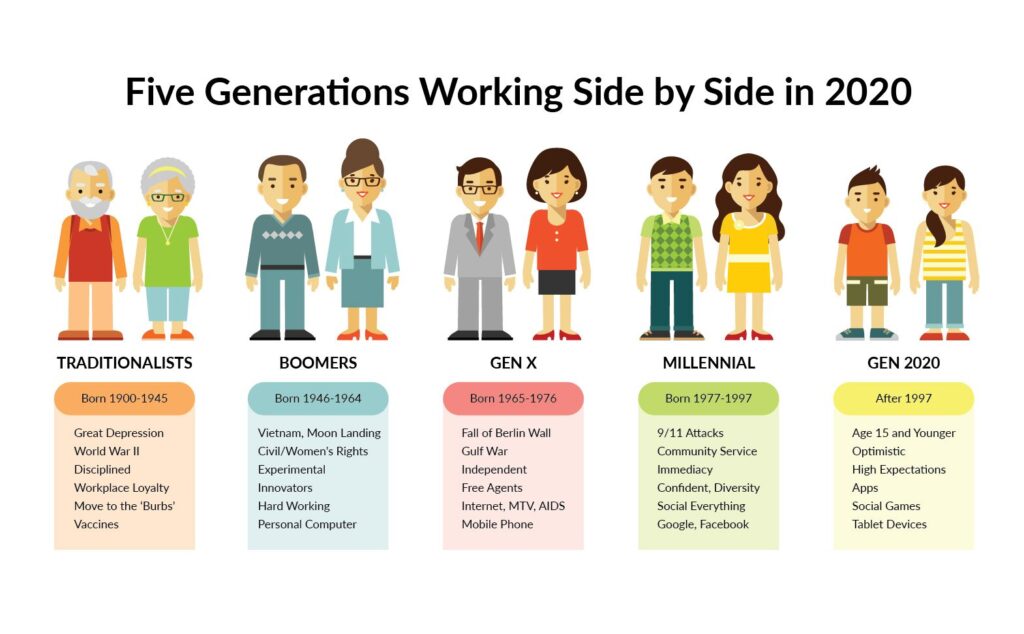
### The Silent Generation (Born 1928-1945)
The Silent Generation, also known as the Traditionalists or the Greatest Generation (overlapping with the WWII generation), grew up during the Great Depression and World War II. These formative experiences instilled in them a strong sense of duty, discipline, and respect for authority. Their traits of the different generations and their characteristics are highly influenced by this.
* **Key Characteristics:** Frugality, hard work, loyalty, respect for rules, civic duty.
* **Values:** Stability, security, conformity, saving money.
* **Work Ethic:** Dedicated, disciplined, and committed to long-term employment.
* **Communication Style:** Formal, respectful, and prefers face-to-face interactions or written communication.
### The Baby Boomers (Born 1946-1964)
The Baby Boomers, a massive generation born after World War II, experienced a period of economic prosperity and social change. They are known for their optimism, competitiveness, and strong work ethic. This generation significantly shaped the modern workplace and consumer culture. Their traits of the different generations and their characteristics reflect their upbringing in an era of optimism and growth.
* **Key Characteristics:** Optimism, ambition, competitiveness, strong work ethic, belief in personal growth.
* **Values:** Materialism, career success, personal fulfillment, social involvement.
* **Work Ethic:** Driven, results-oriented, and willing to work long hours to achieve their goals.
* **Communication Style:** Collaborative, direct, and prefers face-to-face meetings and phone calls.
### Generation X (Born 1965-1980)
Generation X, often referred to as the “latchkey generation,” grew up during a time of economic uncertainty and social upheaval. This led to a sense of independence, resourcefulness, and skepticism. They are known for their adaptability and entrepreneurial spirit. Traits of the different generations and their characteristics in Gen X include a focus on work-life balance.
* **Key Characteristics:** Independence, resourcefulness, skepticism, adaptability, self-reliance.
* **Values:** Work-life balance, personal freedom, informality, practicality.
* **Work Ethic:** Independent, results-oriented, and values flexibility and autonomy.
* **Communication Style:** Direct, informal, and prefers email and instant messaging.
### Millennials (Born 1981-1996)
Millennials, also known as Generation Y, came of age during the rise of the internet and globalization. They are known for their tech-savviness, social consciousness, and desire for meaningful work. Their traits of the different generations and their characteristics are strongly influenced by technology and social media.
* **Key Characteristics:** Tech-savvy, collaborative, socially conscious, optimistic, achievement-oriented.
* **Values:** Purpose, authenticity, experiences, social impact.
* **Work Ethic:** Collaborative, innovative, and seeks opportunities for growth and development.
* **Communication Style:** Digital natives, comfortable with all forms of online communication, including social media, text messaging, and video conferencing.
### Generation Z (Born 1997-2012)
Generation Z, also known as Zoomers, grew up in a hyper-connected world shaped by social media, economic uncertainty, and global events. They are known for their pragmatism, digital fluency, and entrepreneurial mindset. Understanding the traits of the different generations and their characteristics in Gen Z requires acknowledging their digital-first perspective.
* **Key Characteristics:** Digital natives, pragmatic, diverse, entrepreneurial, independent.
* **Values:** Authenticity, inclusivity, financial security, social justice.
* **Work Ethic:** Independent, adaptable, and seeks opportunities for flexibility and entrepreneurship.
* **Communication Style:** Highly visual, prefers short-form content, and utilizes social media platforms like TikTok and Instagram.
### Generation Alpha (Born 2013-2025)
Generation Alpha is the first generation to be born entirely in the 21st century. They are growing up in a world dominated by technology, artificial intelligence, and constant connectivity. While their traits are still developing, early indications suggest they will be highly tech-dependent, globally aware, and accustomed to personalized experiences. The traits of the different generations and their characteristics will continue to evolve as they mature.
* **Key Characteristics:** Tech-dependent, globally aware, personalized experiences, visual learners (projected).
* **Values:** Still developing, but likely to prioritize convenience, personalization, and social impact (projected).
* **Work Ethic:** Unknown, but likely to be highly adaptable and tech-driven (projected).
* **Communication Style:** Highly visual, reliant on technology, and comfortable with virtual interactions (projected).
## Generational Differences in the Workplace
Understanding generational differences is particularly important in the workplace. Each generation brings unique skills, perspectives, and expectations to the table. Recognizing these differences can help foster better communication, collaboration, and overall productivity. Successfully managing the traits of the different generations and their characteristics is a key component of effective leadership.
### Communication Styles
* **Silent Generation & Baby Boomers:** Prefer formal communication, face-to-face meetings, and written memos.
* **Generation X:** Values direct and informal communication, email, and instant messaging.
* **Millennials & Generation Z:** Relies on digital communication, social media, and video conferencing.
### Work Ethic & Values
* **Silent Generation & Baby Boomers:** Dedicated to long-term employment, values loyalty and hard work.
* **Generation X:** Seeks work-life balance and values flexibility and autonomy.
* **Millennials:** Desires meaningful work and opportunities for growth and development.
* **Generation Z:** Prioritizes financial security and seeks opportunities for entrepreneurship and flexibility.
### Management Strategies
* **Tailor communication styles:** Adapt your communication approach to suit the preferences of each generation.
* **Provide opportunities for growth and development:** Offer training programs, mentorship opportunities, and challenging assignments.
* **Foster a culture of inclusivity:** Create a workplace where all generations feel valued and respected.
* **Recognize and reward contributions:** Acknowledge and appreciate the unique skills and perspectives that each generation brings to the table.
## Generational Marketing: Reaching Different Audiences
Understanding generational traits is also crucial for effective marketing. Each generation responds to different messaging, channels, and strategies. Tailoring your marketing efforts to resonate with specific generational values and preferences is essential for success. Understanding the traits of the different generations and their characteristics is paramount for effective marketing strategies.
### Key Considerations
* **Values and Motivations:** Understand what motivates each generation and align your messaging accordingly.
* **Communication Channels:** Utilize the communication channels that each generation prefers.
* **Marketing Strategies:** Employ marketing strategies that resonate with each generation’s values and preferences.
### Examples
* **Silent Generation & Baby Boomers:** Traditional advertising channels like television, print, and radio.
* **Generation X:** Email marketing, targeted online ads, and social media platforms like Facebook.
* **Millennials:** Social media marketing, influencer marketing, and content marketing.
* **Generation Z:** Social media platforms like TikTok and Instagram, short-form video content, and authentic brand messaging.
## Addressing Generational Stereotypes and Misconceptions
It’s important to be aware of and challenge generational stereotypes. Generalizations can be harmful and inaccurate, leading to misunderstandings and conflict. While understanding general traits can be helpful, it’s crucial to remember that individuals within each generation are diverse and unique. A key part of understanding the traits of the different generations and their characteristics involves dispelling common myths.
### Common Stereotypes
* **Silent Generation:** Seen as resistant to change and technologically inept.
* **Baby Boomers:** Perceived as entitled and out of touch.
* **Generation X:** Often labeled as cynical and apathetic.
* **Millennials:** Frequently criticized for being narcissistic and lazy.
* **Generation Z:** Sometimes seen as overly reliant on technology and lacking social skills.
### Overcoming Misconceptions
* **Focus on individual differences:** Recognize that individuals within each generation are diverse and unique.
* **Avoid generalizations:** Challenge stereotypes and avoid making assumptions based on generational labels.
* **Promote intergenerational dialogue:** Encourage open communication and understanding between different generations.
* **Embrace diversity:** Value the unique skills and perspectives that each generation brings to the table.
## Generational Cohort Theory: A Closer Look
The generational cohort theory posits that people born within a specific time period share similar values, beliefs, and behaviors due to shared historical and social experiences. This theory provides a framework for understanding how generational differences can impact various aspects of society, from politics and economics to culture and technology. The traits of the different generations and their characteristics are often analyzed through this lens.
### Key Principles
* **Shared Experiences:** Members of a generation experience similar historical events, cultural trends, and technological advancements.
* **Formative Years:** Experiences during formative years (typically adolescence and early adulthood) have a lasting impact on values and beliefs.
* **Generational Identity:** Shared experiences contribute to a sense of generational identity and shared values.
### Criticisms
* **Oversimplification:** The theory can oversimplify the complexities of human behavior and individual differences.
* **Cultural Bias:** The theory is often based on Western cultural norms and may not be applicable to other cultures.
* **Lack of Empirical Evidence:** Some critics argue that there is limited empirical evidence to support the theory.
## The Future of Generations: Trends and Predictions
As technology continues to evolve and the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the traits of the different generations and their characteristics will continue to evolve. Future generations are likely to be even more tech-dependent, globally aware, and adaptable. Understanding these emerging trends is crucial for navigating the challenges and opportunities of the future.
### Emerging Trends
* **Increased Tech Dependence:** Future generations will grow up in a world where technology is seamlessly integrated into every aspect of life.
* **Globalization:** Increased global connectivity will lead to greater cultural awareness and diversity.
* **Personalization:** Future generations will expect personalized experiences and customized solutions.
* **Sustainability:** Growing awareness of environmental issues will drive a greater focus on sustainability and social responsibility.
### Predictions
* **Generation Beta (Born after 2025):** Likely to be even more tech-savvy and globally connected than previous generations.
* **Emphasis on Skills-Based Learning:** Education will shift towards skills-based learning and personalized learning experiences.
* **Rise of the Gig Economy:** The gig economy will continue to grow, offering greater flexibility and autonomy.
* **Increased Focus on Mental Health:** Mental health awareness will continue to rise, leading to greater support and resources.
## Understanding Generational Trauma and Its Impact
Generational trauma, also known as intergenerational trauma, refers to the transmission of trauma from one generation to the next. Major historical events, such as wars, economic depressions, and social injustices, can have a lasting impact on individuals and communities, and these traumas can be passed down through families and generations. Recognizing the potential impact of generational trauma is important for understanding the traits of the different generations and their characteristics.
### Mechanisms of Transmission
* **Genetic Inheritance:** Emerging research suggests that trauma can alter gene expression and be passed down through epigenetic inheritance.
* **Parenting Styles:** Traumatized parents may exhibit parenting styles that perpetuate trauma, such as emotional unavailability or overprotectiveness.
* **Cultural Narratives:** Cultural narratives and historical accounts can transmit trauma across generations.
### Impact on Generations
* **Increased Risk of Mental Health Issues:** Individuals from traumatized generations may be at higher risk of developing anxiety, depression, and PTSD.
* **Difficulties with Attachment and Relationships:** Trauma can interfere with the ability to form healthy attachments and relationships.
* **Sense of Disconnection:** Individuals may feel disconnected from their families, communities, and cultural heritage.
## Bridging Generational Gaps: Strategies for Better Understanding
Bridging generational gaps requires empathy, understanding, and a willingness to learn from one another. By recognizing and appreciating the unique skills, perspectives, and experiences of each generation, we can foster better communication, collaboration, and overall harmony. Understanding the traits of the different generations and their characteristics is the first step toward building stronger relationships.
### Practical Strategies
* **Active Listening:** Practice active listening and try to understand the perspectives of others.
* **Empathy:** Put yourself in the shoes of someone from a different generation and try to understand their experiences.
* **Open Communication:** Encourage open and honest communication and create a safe space for dialogue.
* **Respect:** Treat others with respect, regardless of their age or background.
* **Mentorship:** Create mentorship programs that pair younger and older generations together.
* **Reverse Mentoring:** Encourage younger employees to mentor older employees on technology and social media.
## Conclusion: Embracing Generational Diversity for a Better Future
Understanding the traits of the different generations and their characteristics is essential for navigating the complexities of today’s interconnected world. By recognizing and appreciating the unique skills, perspectives, and experiences of each generation, we can foster better communication, collaboration, and overall harmony. Embracing generational diversity is not just a matter of tolerance; it’s a strategic advantage that can lead to greater innovation, creativity, and success. As we look to the future, it’s crucial to continue learning from one another and building bridges across generational divides. Now, share your experiences with generational dynamics in the comments below and let’s continue this important conversation.