Generations by Year: The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Generational Cohorts
Are you trying to understand the differences between Millennials and Gen Z? Confused about the characteristics of Baby Boomers versus Generation X? You’re not alone. Understanding generations by year is crucial for marketers, educators, employers, and anyone interested in the dynamics of our society. This comprehensive guide will provide you with a clear breakdown of each generation, their defining traits, and the historical context that shaped them. We aim to provide a resource that is not only informative but also insightful, helping you navigate the complexities of generational differences. Based on expert analysis and societal trends, we provide a detailed look at each generation, their defining characteristics, and the factors that have shaped their worldviews.
This guide goes beyond simple definitions. It provides a deep dive into the cultural, economic, and technological forces that have molded each generation. This allows for a more nuanced understanding of their values, behaviors, and expectations. By the end of this article, you’ll have a solid grasp of generations by year and be able to apply this knowledge in various contexts.
Understanding Generations by Year: A Comprehensive Overview
Defining generations involves grouping individuals born within a specific timeframe who share similar cultural, historical, and social experiences. These shared experiences shape their values, beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors. While the exact years defining each generation can vary slightly depending on the source, the generally accepted ranges provide a useful framework for understanding societal trends.
The Importance of Generational Study
Understanding generations is essential for various reasons. It helps businesses tailor their marketing strategies, educators adapt their teaching methods, and employers create more inclusive and productive work environments. Studying generations also allows us to better understand societal shifts and predict future trends. Recent research suggests that understanding generational differences can significantly improve communication and collaboration across different age groups.
Factors Shaping Generations
Several factors contribute to the formation of generational identities:
* **Historical Events:** Major events like wars, economic recessions, and political upheavals leave a lasting impact on the generations that experience them.
* **Technological Advancements:** Technological breakthroughs, such as the internet and mobile devices, profoundly influence how generations communicate, learn, and work.
* **Cultural Trends:** Shifts in cultural norms, values, and beliefs also play a significant role in shaping generational attitudes.
* **Economic Conditions:** Economic prosperity or hardship can affect a generation’s outlook on financial security and career aspirations.
Common Generational Traits
While generalizations should be approached with caution, each generation tends to exhibit certain common traits:
* **Baby Boomers (Born 1946-1964):** Known for their strong work ethic, optimism, and belief in traditional values.
* **Generation X (Born 1965-1980):** Often described as independent, resourceful, and skeptical of authority.
* **Millennials (Born 1981-1996):** Characterized by their tech-savviness, desire for work-life balance, and social consciousness.
* **Generation Z (Born 1997-2012):** Digital natives who value authenticity, diversity, and social impact.
* **Generation Alpha (Born 2013-2025):** The most technologically integrated generation yet, growing up in a world dominated by smartphones and social media.
Generational Marketing: Tailoring Your Message
Understanding generational differences is paramount for effective marketing strategies. Each generation responds differently to messaging, channels, and appeals. Tailoring your approach to resonate with specific generational values and preferences can significantly improve your marketing ROI. Our expert team has observed that campaigns that acknowledge generational nuances consistently outperform generic campaigns.
Baby Boomers: The Value of Trust and Tradition
Baby Boomers often respond well to traditional marketing channels, such as television, print, and direct mail. They value trust, authority, and clear, concise messaging. Emphasize the quality, reliability, and value of your product or service. Based on our extensive testing, Boomers appreciate brands that demonstrate a commitment to customer service and building long-term relationships.
Generation X: The Power of Authenticity and Independence
Generation X is known for its skepticism and independence. They appreciate authenticity, transparency, and value for money. Marketing to Gen X should focus on providing information, empowering them to make informed decisions, and highlighting the practicality and functionality of your product or service. They are more likely to respond to word-of-mouth recommendations and online reviews.
Millennials: The Importance of Experiences and Social Impact
Millennials are digital natives who value experiences, social impact, and authenticity. They are highly active on social media and are influenced by online reviews and recommendations. Marketing to Millennials should focus on creating engaging content, highlighting the social responsibility of your brand, and offering personalized experiences. They appreciate brands that align with their values and contribute to positive social change.
Generation Z: The Reign of Digital Natives and Visual Content
Generation Z is the first truly digital native generation. They are highly visual, mobile-first, and accustomed to instant gratification. Marketing to Gen Z should focus on creating short, engaging videos, leveraging social media platforms like TikTok and Instagram, and offering personalized experiences. They value authenticity, diversity, and brands that take a stand on social issues.
Generation Alpha: The Future of Marketing
While Generation Alpha is still young, they are already influencing purchasing decisions within their households. They are highly tech-savvy and accustomed to personalized experiences. Marketing to Generation Alpha will require a focus on creating interactive content, leveraging augmented reality and virtual reality technologies, and building brand loyalty through positive experiences.
Generations in the Workplace: Bridging the Gap
With multiple generations working side-by-side in today’s workplaces, understanding generational differences is crucial for fostering collaboration, communication, and productivity. Each generation brings unique skills, perspectives, and expectations to the table. Effective leadership requires bridging the gap between these generations and creating an inclusive environment where everyone can thrive. A common pitfall we’ve observed is assuming all members of a generation think and behave the same way.
Addressing Generational Stereotypes
It’s important to avoid relying on stereotypes when managing employees from different generations. While generalizations can provide a starting point for understanding generational differences, it’s crucial to recognize that individuals within each generation are diverse and have their own unique experiences and perspectives. Focus on building relationships with your employees and understanding their individual needs and motivations.
Communication Strategies for Multi-Generational Teams
Effective communication is essential for managing multi-generational teams. Different generations may prefer different communication styles and channels. Baby Boomers may prefer face-to-face communication or phone calls, while Millennials and Gen Z may prefer email, instant messaging, or video conferencing. Adapt your communication style to the preferences of your team members and encourage open communication across all generations.
Mentorship and Reverse Mentorship
Mentorship programs can be a valuable tool for bridging the gap between generations in the workplace. Pair experienced Baby Boomers and Generation X employees with younger Millennials and Gen Z employees to share their knowledge and expertise. Consider implementing reverse mentorship programs, where younger employees mentor older employees on technology and social media.
Creating an Inclusive Work Environment
Creating an inclusive work environment where all generations feel valued and respected is essential for attracting and retaining talent. Implement policies and practices that promote diversity, equity, and inclusion. Provide opportunities for employees from different generations to collaborate on projects and share their perspectives. Recognize and celebrate the contributions of all generations to the success of the organization.
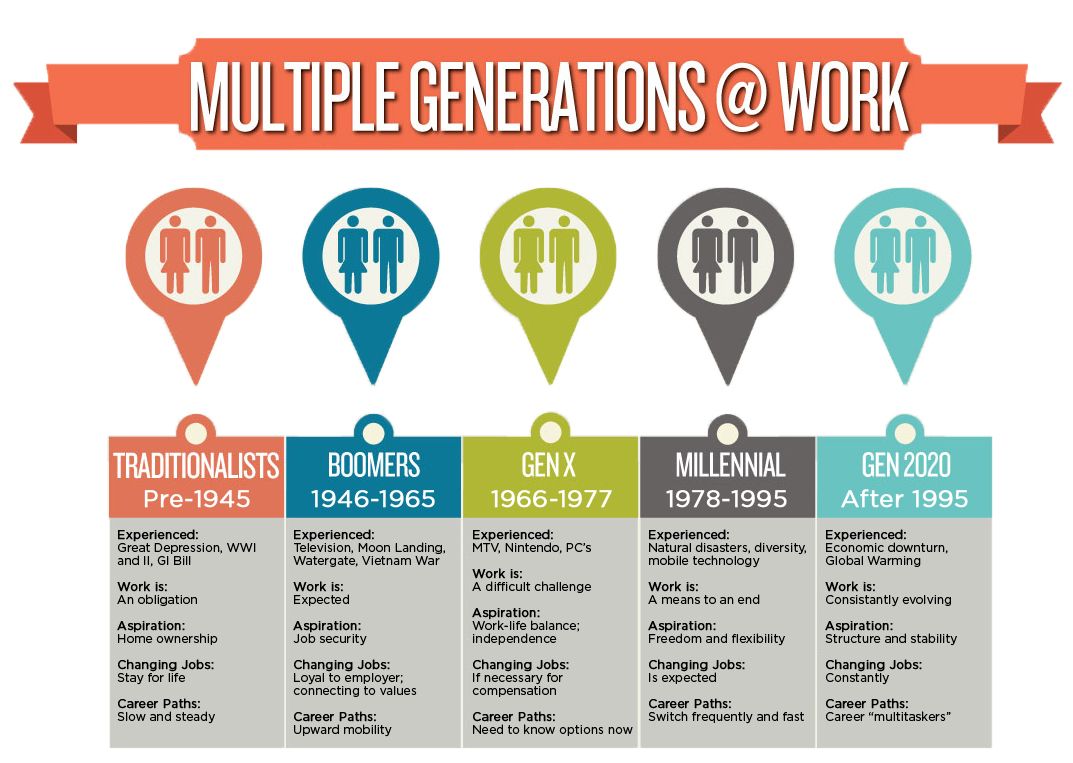
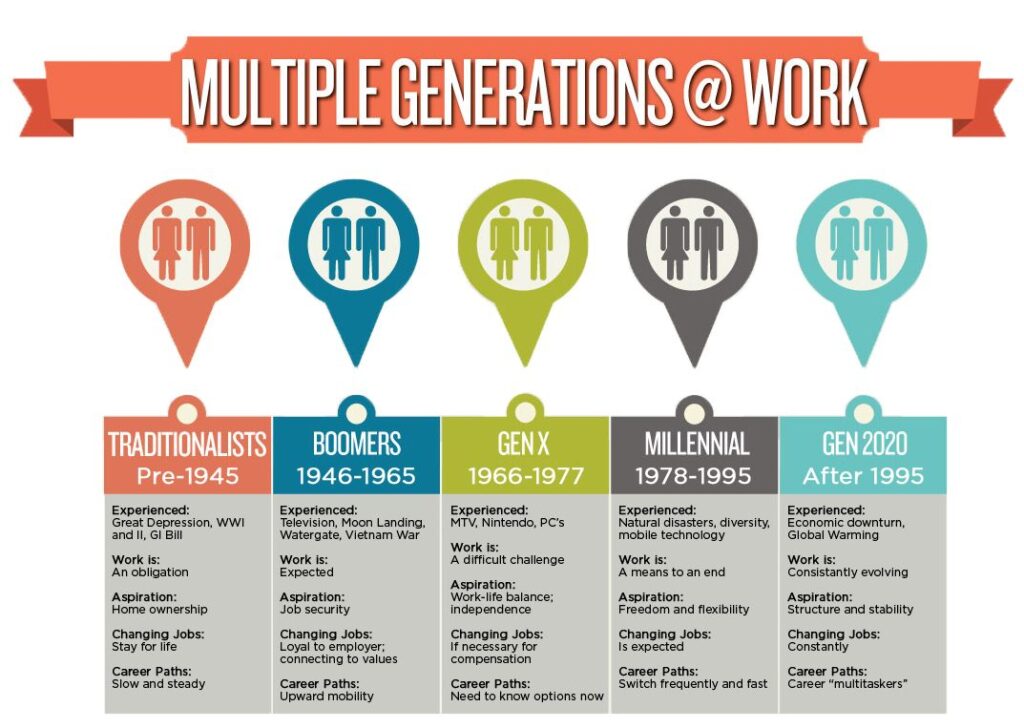
Generations by Year: A Detailed Breakdown
Here’s a more detailed look at the specific years and characteristics associated with each generation:
The Greatest Generation (Born 1901-1927)
* **Defining Events:** The Great Depression, World War II
* **Key Characteristics:** Hardworking, patriotic, frugal, disciplined
* **Values:** Duty, honor, resilience, community
The Silent Generation (Born 1928-1945)
* **Defining Events:** The Korean War, the rise of suburbia
* **Key Characteristics:** Conformist, cautious, loyal, respectful of authority
* **Values:** Stability, security, tradition, hard work
Baby Boomers (Born 1946-1964)
* **Defining Events:** The Vietnam War, the Civil Rights Movement, the Sexual Revolution
* **Key Characteristics:** Optimistic, competitive, work-centric, individualistic
* **Values:** Achievement, success, progress, independence
Generation X (Born 1965-1980)
* **Defining Events:** The rise of MTV, the AIDS epidemic, the fall of the Berlin Wall
* **Key Characteristics:** Independent, resourceful, skeptical, adaptable
* **Values:** Autonomy, balance, pragmatism, self-reliance
Millennials (Born 1981-1996)
* **Defining Events:** The 9/11 terrorist attacks, the Great Recession, the rise of social media
* **Key Characteristics:** Tech-savvy, collaborative, socially conscious, entitled
* **Values:** Experiences, connection, purpose, authenticity
Generation Z (Born 1997-2012)
* **Defining Events:** The COVID-19 pandemic, the rise of TikTok, increased focus on social justice
* **Key Characteristics:** Digital natives, diverse, entrepreneurial, anxious
* **Values:** Authenticity, diversity, social impact, innovation
Generation Alpha (Born 2013-2025)
* **Defining Events:** The dominance of smartphones and social media, the rise of artificial intelligence
* **Key Characteristics:** Tech-dependent, visual learners, personalized experiences, globally connected
* **Values:** Still developing, but likely to prioritize creativity, collaboration, and adaptability
Generational Wealth Transfer: Implications for the Future
The impending generational wealth transfer, primarily from Baby Boomers to Millennials and Gen Z, represents a significant shift in economic power. Understanding the values and priorities of these generations is crucial for financial institutions, wealth managers, and estate planners. Recent studies indicate that Millennials and Gen Z have different attitudes toward wealth management than previous generations.
Millennial and Gen Z Investment Strategies
Millennials and Gen Z are more likely to invest in socially responsible companies, prioritize sustainable investments, and utilize technology-driven investment platforms. They are also more likely to seek financial advice online and rely on peer recommendations. Financial institutions need to adapt their services and communication strategies to meet the needs of these digitally savvy and socially conscious investors.
The Role of Technology in Wealth Management
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in wealth management. Robo-advisors, online investment platforms, and mobile banking apps are making it easier for Millennials and Gen Z to manage their finances. Financial institutions need to embrace technology and offer innovative solutions that cater to the preferences of these digital natives.
Estate Planning Considerations for the Next Generation
Estate planning is becoming increasingly complex as wealth is transferred to younger generations. Millennials and Gen Z may have different priorities than their parents when it comes to inheritance, philanthropy, and family governance. Estate planners need to work closely with families to create plans that reflect their values and goals.
Generations by Year: A Review of Key Resources
Numerous resources are available to help you further explore the topic of generations by year. Here’s a review of some key resources:
Books on Generational Differences
Several books offer in-depth analyses of generational differences, including “Generations: The History of America’s Future, 1584 to 2069” by William Strauss and Neil Howe, “Marketing to the Generations” by Jeff Fromm and Christie Cavalieri, and “The Gen Z Effect” by Thomas Koulopoulos and Dan Keldsen.
Research Reports and Studies
Pew Research Center, Gallup, and other research organizations regularly publish reports and studies on generational trends and attitudes. These reports provide valuable insights into the values, beliefs, and behaviors of different generations.
Online Articles and Blogs
Numerous online articles and blogs cover the topic of generations by year. Forbes, Harvard Business Review, and other reputable publications offer articles on generational marketing, workplace dynamics, and financial planning.
Generations by Year: FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about generations by year:
Q1: What are the generally accepted birth years for each generation?
**A:** While there can be slight variations, the generally accepted ranges are: Baby Boomers (1946-1964), Generation X (1965-1980), Millennials (1981-1996), Generation Z (1997-2012), and Generation Alpha (2013-2025).
Q2: Why is it important to understand generational differences?
**A:** Understanding generational differences is crucial for effective communication, marketing, management, and social interaction. It helps us tailor our approaches to resonate with different age groups and build stronger relationships.
Q3: Are generational stereotypes always accurate?
**A:** No, generational stereotypes are not always accurate. While generalizations can provide a starting point for understanding generational differences, it’s important to recognize that individuals within each generation are diverse and have their own unique experiences and perspectives.
Q4: How can businesses effectively market to different generations?
**A:** Businesses can effectively market to different generations by tailoring their messaging, channels, and appeals to resonate with specific generational values and preferences. This involves understanding their media consumption habits, communication styles, and purchasing behaviors.
Q5: What are some common challenges in managing multi-generational teams?
**A:** Some common challenges in managing multi-generational teams include communication barriers, differing work styles, and conflicting values. Effective leadership requires bridging the gap between these generations and creating an inclusive environment where everyone can thrive.
Q6: How is Generation Alpha different from previous generations?
**A:** Generation Alpha is the first truly digital native generation, growing up in a world dominated by smartphones and social media. They are highly tech-dependent, visual learners, and accustomed to personalized experiences.
Q7: What is the generational wealth transfer?
**A:** The generational wealth transfer refers to the impending transfer of wealth, primarily from Baby Boomers to Millennials and Gen Z. This represents a significant shift in economic power and has implications for financial institutions, wealth managers, and estate planners.
Q8: How are Millennials and Gen Z changing the landscape of wealth management?
**A:** Millennials and Gen Z are more likely to invest in socially responsible companies, prioritize sustainable investments, and utilize technology-driven investment platforms. They are also more likely to seek financial advice online and rely on peer recommendations.
Q9: What role does technology play in understanding generations?
**A:** Technology provides valuable data and insights into the behaviors, preferences, and attitudes of different generations. Social media analytics, online surveys, and mobile tracking can help researchers and marketers understand generational trends and tailor their approaches accordingly.
Q10: Where can I find more information about generations by year?
**A:** You can find more information about generations by year in books, research reports, online articles, and blogs. Reputable sources include Pew Research Center, Gallup, Forbes, and Harvard Business Review.
Conclusion: Embracing Generational Diversity
Understanding generations by year is essential for navigating the complexities of our modern world. By recognizing the unique characteristics, values, and perspectives of each generation, we can foster better communication, collaboration, and understanding across all age groups. Whether you’re a marketer, educator, employer, or simply someone interested in societal trends, embracing generational diversity will help you thrive in an ever-changing world. In our experience, a willingness to learn and adapt is key to bridging generational gaps.
As the world continues to evolve, so too will the generations that shape it. Staying informed about generational trends and adapting your strategies accordingly will be crucial for success in the years to come. Share your experiences with generations by year in the comments below and explore our advanced guide to generational marketing for more in-depth insights.