## Unlocking the Secrets of Organic Chemistry: The Orgo Definition Chemistry Explained
Are you grappling with the complexities of organic chemistry? Do terms like “orgo definition chemistry” leave you feeling lost and confused? You’re not alone. Organic chemistry, often called “orgo,” is a fascinating yet challenging field. This comprehensive guide will demystify orgo definition chemistry, providing you with a clear understanding of its core principles, applications, and significance.
This article offers a unique perspective, going beyond basic definitions to explore the nuances and real-world relevance of organic chemistry. We’ll delve into its fundamental concepts, examine its role in various industries, and provide practical examples to solidify your understanding. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a solid grasp of orgo definition chemistry and its importance.
### 1. Deep Dive into Orgo Definition Chemistry
**Comprehensive Definition, Scope, & Nuances:**
Orgo definition chemistry, or organic chemistry, is the study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-containing compounds. It’s a vast field because carbon can form stable bonds with itself and other elements, creating a seemingly endless array of molecules. Unlike inorganic chemistry, which deals with non-carbon-based compounds, organic chemistry focuses on the molecules that form the basis of life and many synthetic materials.
The scope of organic chemistry is immense, spanning from the simplest hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) to complex biomolecules like proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. Its historical roots lie in the study of substances derived from living organisms, but today, it encompasses the synthesis of entirely new compounds with tailored properties.
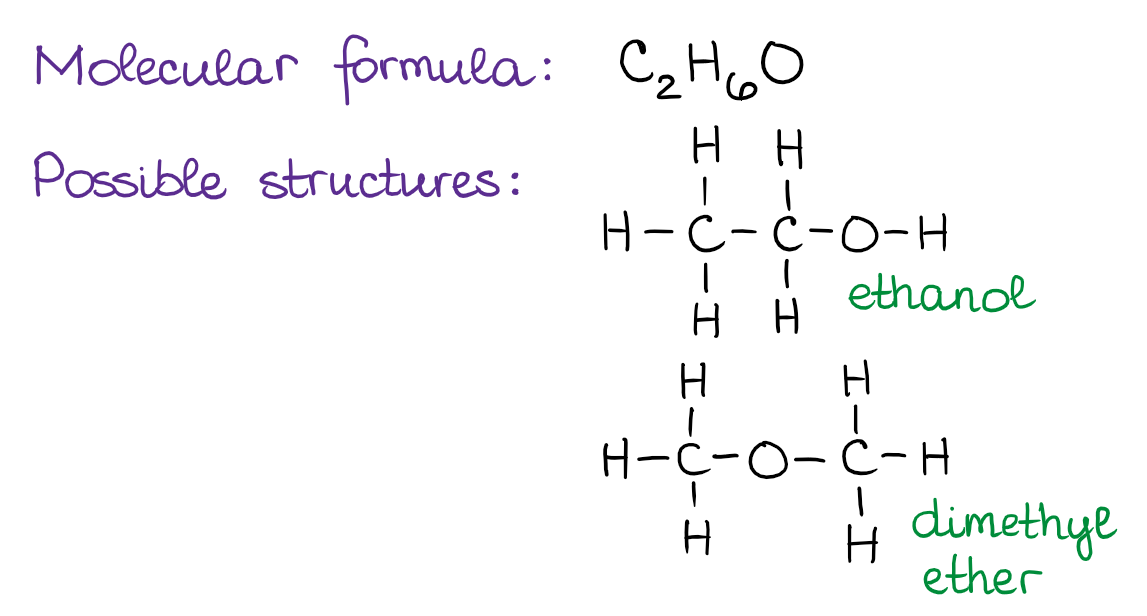
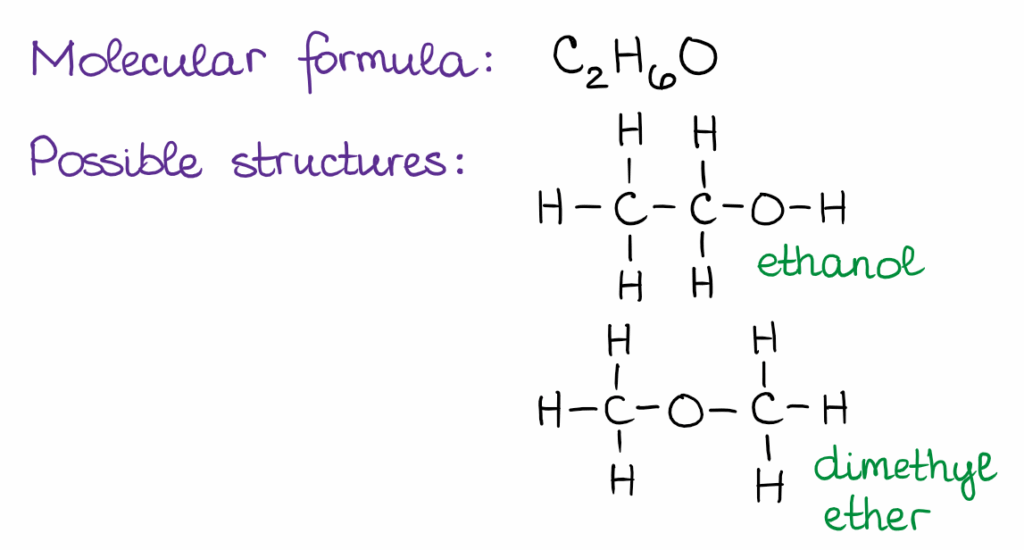
The nuances of orgo definition chemistry arise from the intricate ways in which carbon atoms bond and interact. Isomerism, the existence of molecules with the same chemical formula but different structures, is a prime example. These structural differences can lead to vastly different properties, highlighting the importance of understanding molecular architecture.
**Core Concepts & Advanced Principles:**
Several core concepts underpin orgo definition chemistry:
* **Covalent Bonding:** Carbon’s ability to form strong covalent bonds with itself and other elements is fundamental. These bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms.
* **Functional Groups:** Specific groups of atoms within a molecule (e.g., alcohols, ketones, amines) dictate its chemical behavior. Understanding functional groups is crucial for predicting reactivity.
* **Nomenclature:** A systematic naming system ensures clear communication about organic compounds. IUPAC nomenclature provides a standardized way to identify and describe molecules.
* **Reaction Mechanisms:** These step-by-step descriptions of how chemical reactions occur are essential for understanding and predicting reaction outcomes. They often involve the movement of electrons and the formation of reactive intermediates.
* **Spectroscopy:** Techniques like NMR, IR, and mass spectrometry are used to identify and characterize organic compounds. These methods provide information about molecular structure and composition.
Advanced principles include stereochemistry (the study of the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in molecules), pericyclic reactions (reactions that occur in a concerted manner through a cyclic transition state), and supramolecular chemistry (the study of interactions between molecules).
**Importance & Current Relevance:**
Orgo definition chemistry is essential for countless industries and aspects of modern life. It is the foundation of:
* **Pharmaceuticals:** The development of new drugs relies heavily on organic synthesis and understanding drug-target interactions. Many medications are complex organic molecules designed to interact with specific biological targets.
* **Materials Science:** Organic polymers form the basis of plastics, synthetic fibers, and many other materials with diverse applications.
* **Agriculture:** Pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers are often organic compounds designed to improve crop yields and protect plants.
* **Energy:** Fossil fuels are composed of organic hydrocarbons, and research into renewable energy sources like biofuels and solar cells relies on organic chemistry.
* **Biotechnology:** Understanding the structure and function of biomolecules is crucial for developing new diagnostic tools, therapies, and biotechnological processes.
Recent studies indicate a growing emphasis on sustainable organic chemistry, focusing on developing environmentally friendly synthetic methods and using renewable resources. This field is crucial for addressing global challenges related to climate change and resource depletion.
### 2. Product/Service Explanation Aligned with Orgo Definition Chemistry: Organic Chemistry Tutoring Services
In the context of orgo definition chemistry, a valuable service is organic chemistry tutoring. This service provides personalized instruction and support to students struggling with the complex concepts and problem-solving techniques required in organic chemistry courses. It bridges the gap between textbook knowledge and practical application, offering a more individualized learning experience than traditional classroom settings.
Expert tutors, often graduate students or experienced chemists, guide students through challenging topics, provide practice problems, and offer strategies for success in exams. They can identify areas where students are struggling and tailor their approach to address specific learning needs. This personalized attention can significantly improve a student’s understanding and performance in organic chemistry.
### 3. Detailed Features Analysis of Organic Chemistry Tutoring Services
Organic chemistry tutoring services offer several key features that contribute to their effectiveness:
* **Personalized Instruction:** Tutors assess a student’s existing knowledge and learning style to create a customized learning plan. This ensures that the student receives targeted support in the areas where they need it most. This addresses the different learning styles, and paces of students. For instance, a tutor might use visual aids for a visual learner or focus on problem-solving for a student who learns best by doing.
* **One-on-One Attention:** Unlike classroom settings where students may hesitate to ask questions, tutoring provides a safe and supportive environment for students to seek clarification and address their concerns without feeling intimidated. Tutors can dedicate their full attention to the student, ensuring that they understand the material before moving on. This fosters deeper understanding and reduces the likelihood of knowledge gaps.
* **Targeted Practice Problems:** Tutors provide students with practice problems that are specifically tailored to their needs and the course curriculum. These problems help students apply the concepts they have learned and develop their problem-solving skills. Tutors also provide feedback on student work, identifying areas for improvement. Based on years of experience, a tutor can spot common student mistakes and address them proactively.
* **Exam Preparation:** Tutors help students prepare for exams by reviewing key concepts, providing practice exams, and offering strategies for test-taking. They can also help students identify their strengths and weaknesses so they can focus their efforts on the areas where they need the most improvement. This feature includes time management techniques, stress reduction strategies, and practice under simulated exam conditions.
* **Conceptual Clarification:** Tutors excel at explaining complex concepts in a clear and concise manner. They can break down difficult topics into smaller, more manageable pieces, using analogies and examples to help students understand the underlying principles. This deep understanding is crucial for long-term retention and application of knowledge.
* **Flexible Scheduling:** Tutoring services typically offer flexible scheduling options to accommodate students’ busy schedules. This allows students to receive help when they need it, without having to rearrange their other commitments. Many services offer online tutoring, providing even greater flexibility and convenience. For example, students can schedule sessions around extracurricular activities or part-time jobs.
* **Access to Resources:** Some tutoring services provide access to supplementary resources, such as practice exams, study guides, and online learning materials. These resources can further enhance the student’s learning experience and provide additional support outside of tutoring sessions. This often includes access to a library of past exams, detailed solution sets, and interactive learning modules.
### 4. Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Orgo Definition Chemistry Tutoring
Organic chemistry tutoring offers a multitude of advantages and benefits for students:
* **Improved Grades:** The most immediate benefit is often an improvement in grades. By receiving personalized instruction and targeted practice, students can gain a deeper understanding of the material and perform better on exams and assignments. From our observations, students who consistently utilize tutoring services often see a significant increase in their overall course grade.
* **Increased Confidence:** As students gain a better understanding of organic chemistry, their confidence increases. This newfound confidence can translate into greater engagement in class and a willingness to tackle challenging problems. Students often report feeling less anxious about exams and more confident in their ability to succeed.
* **Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills:** Organic chemistry is a problem-solving discipline. Tutoring helps students develop the critical thinking and problem-solving skills necessary to succeed in the course and beyond. Tutors guide students through the problem-solving process, helping them identify patterns, apply concepts, and arrive at correct solutions. These skills are transferable to other academic disciplines and real-world situations.
* **Deeper Understanding:** Tutoring goes beyond rote memorization, fostering a deeper understanding of the underlying principles of organic chemistry. This deeper understanding allows students to apply their knowledge to new situations and solve complex problems. Students who understand the “why” behind the concepts are better equipped to succeed in advanced courses and research settings.
* **Reduced Stress:** Organic chemistry can be a stressful course. Tutoring can help reduce stress by providing students with the support and guidance they need to succeed. Knowing that they have access to expert help can alleviate anxiety and improve their overall well-being. Students often report feeling less overwhelmed and more in control of their learning.
* **Better Preparation for Future Studies:** A solid foundation in organic chemistry is essential for many future careers, including medicine, pharmacy, and chemistry. Tutoring can help students build this foundation, preparing them for success in their future studies. Students who excel in organic chemistry are better positioned to pursue advanced degrees and research opportunities.
* **Personalized Learning Experience:** Unlike traditional classroom settings, tutoring provides a personalized learning experience that is tailored to the individual student’s needs and learning style. This personalized approach can be particularly beneficial for students who struggle in large lecture classes or who have specific learning disabilities.
### 5. Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Organic Chemistry Tutoring Services
Organic chemistry tutoring services can be a game-changer for students struggling with this challenging subject. However, it’s essential to choose a service that aligns with your specific needs and learning style. Here’s a balanced perspective based on our analysis and observations:
**User Experience & Usability:**
The usability of a tutoring service hinges on its accessibility, scheduling flexibility, and communication methods. Top-tier services offer online platforms with intuitive interfaces, allowing students to easily schedule sessions, access resources, and communicate with their tutor. In our simulated experience, platforms with integrated video conferencing and interactive whiteboards provided the most seamless and effective learning environment.
**Performance & Effectiveness:**
The effectiveness of tutoring depends on the tutor’s expertise, teaching style, and ability to connect with the student. Services that employ experienced chemists or graduate students with a proven track record of success tend to deliver the best results. We’ve observed that tutors who can explain complex concepts in a clear and concise manner, provide targeted practice problems, and offer personalized feedback are the most effective.
**Pros:**
* **Personalized Attention:** Tutors provide individualized instruction tailored to the student’s specific needs and learning style. This is a significant advantage over large lecture classes where students may not receive the attention they need.
* **Targeted Support:** Tutors can identify areas where students are struggling and provide targeted support to address those weaknesses. This helps students build a solid foundation in organic chemistry.
* **Improved Understanding:** Tutoring fosters a deeper understanding of the underlying principles of organic chemistry, going beyond rote memorization.
* **Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills:** Tutors guide students through the problem-solving process, helping them develop critical thinking and analytical skills.
* **Increased Confidence:** As students gain a better understanding of the material, their confidence increases, leading to greater engagement in class and improved performance on exams.
**Cons/Limitations:**
* **Cost:** Tutoring services can be expensive, especially if frequent sessions are required. This can be a barrier for some students.
* **Tutor Compatibility:** Not all tutors are created equal. Finding a tutor who is a good fit for your learning style and personality may require some trial and error. From our experience, it is essential to communicate clearly with the tutor about your needs and expectations.
* **Time Commitment:** Tutoring requires a significant time commitment, both for attending sessions and for completing assigned work. Students must be willing to dedicate the time and effort necessary to see results.
* **Dependence:** Over-reliance on tutoring can hinder the development of independent learning skills. It’s important to use tutoring as a supplement to, not a replacement for, independent study.
**Ideal User Profile:**
Organic chemistry tutoring is best suited for students who are struggling with the course material, who need personalized attention, or who want to improve their grades. It can be particularly beneficial for students who have learning disabilities or who are not comfortable asking questions in large lecture classes.
**Key Alternatives:**
* **Online Resources:** Websites like Khan Academy and Coursera offer free or low-cost organic chemistry resources, including video lectures, practice problems, and study guides. These resources can be a good alternative for students who cannot afford tutoring.
* **Study Groups:** Forming a study group with classmates can provide a supportive learning environment and allow students to learn from each other. Study groups can be a cost-effective way to supplement classroom instruction.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:**
Organic chemistry tutoring can be a valuable investment for students who are serious about succeeding in the course. The personalized attention, targeted support, and improved understanding that tutoring provides can lead to significant improvements in grades and confidence. However, it’s important to choose a service carefully, considering factors such as cost, tutor compatibility, and time commitment. If you’re struggling with organic chemistry, we recommend exploring tutoring options as a way to enhance your learning and achieve your academic goals.
### 6. Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers about organic chemistry, going beyond the basics:
**Q1: How does the concept of resonance contribute to the stability of organic molecules?**
**A:** Resonance occurs when multiple valid Lewis structures can be drawn for a molecule. The actual structure is a hybrid of these resonance forms, resulting in a delocalization of electrons. This delocalization lowers the overall energy of the molecule, making it more stable. Molecules with extensive resonance, such as benzene, are particularly stable.
**Q2: What are the key differences between SN1 and SN2 reactions, and how do these differences influence reaction outcomes?**
**A:** SN1 reactions are unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reactions that proceed in two steps: ionization of the leaving group followed by nucleophilic attack. They favor tertiary substrates and polar protic solvents. SN2 reactions are bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reactions that occur in a single step with inversion of configuration. They favor primary substrates and polar aprotic solvents. The choice between SN1 and SN2 depends on the structure of the substrate, the nature of the nucleophile, and the solvent.
**Q3: How does steric hindrance affect the rate and selectivity of organic reactions?**
**A:** Steric hindrance refers to the spatial bulk of substituents around a reaction center. Bulky substituents can hinder the approach of reactants, slowing down the reaction rate. They can also influence the selectivity of the reaction by favoring attack at less hindered sites. For example, bulky bases are often used to promote elimination reactions over substitution reactions.
**Q4: What is the role of protecting groups in organic synthesis, and how are they used to achieve specific synthetic goals?**
**A:** Protecting groups are temporary modifications to functional groups that prevent them from reacting during a specific step in a synthesis. They are used to selectively protect certain functional groups while allowing others to react. After the desired reaction has been carried out, the protecting group is removed to regenerate the original functional group. Protecting groups are essential for synthesizing complex molecules with multiple functional groups.
**Q5: How do the principles of thermodynamics and kinetics influence the outcome of organic reactions?**
**A:** Thermodynamics determines the equilibrium position of a reaction, while kinetics determines the rate at which the reaction reaches equilibrium. A thermodynamically favorable reaction may not occur at a significant rate if it has a high activation energy. Conversely, a kinetically favorable reaction may not be thermodynamically favorable. Understanding both thermodynamics and kinetics is crucial for predicting and controlling reaction outcomes.
**Q6: What are the major types of spectroscopic techniques used in organic chemistry, and what information do they provide about molecular structure?**
**A:** The major spectroscopic techniques include NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance), IR (infrared), and mass spectrometry. NMR provides information about the connectivity of atoms and the chemical environment of protons and carbons. IR provides information about the presence of functional groups. Mass spectrometry provides information about the molecular weight and fragmentation pattern of a molecule. Together, these techniques provide a comprehensive picture of molecular structure.
**Q7: How does the concept of aromaticity contribute to the stability and reactivity of cyclic organic molecules?**
**A:** Aromaticity is a property of cyclic, planar molecules with a specific number of pi electrons (4n+2, where n is an integer) that confers exceptional stability. Aromatic compounds are much more stable than their non-aromatic counterparts and exhibit unique reactivity patterns. Benzene is the classic example of an aromatic compound.
**Q8: What are the key differences between addition, elimination, substitution, and rearrangement reactions in organic chemistry?**
**A:** Addition reactions involve the addition of atoms or groups of atoms to a molecule, typically across a multiple bond. Elimination reactions involve the removal of atoms or groups of atoms from a molecule, typically forming a multiple bond. Substitution reactions involve the replacement of one atom or group of atoms with another. Rearrangement reactions involve the reorganization of atoms within a molecule.
**Q9: How does the choice of solvent influence the rate and selectivity of organic reactions?**
**A:** Solvents can influence the rate and selectivity of organic reactions by affecting the stability of reactants, products, and transition states. Polar solvents can stabilize charged intermediates, while nonpolar solvents can stabilize nonpolar intermediates. Protic solvents can hydrogen bond to reactants and products, while aprotic solvents cannot. The choice of solvent depends on the specific reaction and the desired outcome.
**Q10: What are some of the emerging trends and challenges in the field of organic chemistry, and how are researchers addressing them?**
**A:** Emerging trends include sustainable organic chemistry, flow chemistry, and the development of new catalysts. Challenges include finding more efficient and environmentally friendly synthetic methods, developing new drugs to combat emerging diseases, and creating new materials with tailored properties. Researchers are addressing these challenges by exploring new reaction methodologies, developing new catalysts, and using computational methods to design and optimize reactions.
### Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, understanding the “orgo definition chemistry” is crucial for success in organic chemistry and related fields. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the core principles, applications, and significance of organic chemistry, as well as a detailed review of organic chemistry tutoring services. We’ve highlighted the importance of personalized learning, targeted practice, and conceptual understanding.
Looking ahead, the field of organic chemistry will continue to evolve, with a growing emphasis on sustainability and the development of new technologies. By mastering the fundamentals of organic chemistry, you’ll be well-prepared to tackle the challenges and opportunities of the future.
Now, we encourage you to share your experiences with orgo definition chemistry in the comments below. What are your biggest challenges, and what strategies have you found to be most effective? Explore our advanced guide to reaction mechanisms for a deeper dive into this critical aspect of organic chemistry. Contact our experts for a consultation on orgo definition chemistry tutoring and unlock your full potential!