## Premature Ventricular Contractions ICD-10: The Expert’s Guide to Understanding and Managing PVCs
Are you experiencing heart palpitations or have you been diagnosed with premature ventricular contractions (PVCs)? Understanding the ICD-10 code associated with this condition is crucial for proper diagnosis, treatment, and insurance coverage. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth look at PVCs, their ICD-10 coding, diagnosis, management, and the latest advancements in treatment. We aim to provide unparalleled clarity and actionable insights, drawing from expert consensus and clinical experience, to empower you with the knowledge you need to navigate this condition effectively. This resource offers unique value by synthesizing complex medical information into an accessible format, focusing on both the clinical aspects and the practical implications of PVCs and their coding, reflecting our commitment to providing trustworthy, expert-driven guidance.
## Understanding Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs) and the ICD-10 Code
### What are Premature Ventricular Contractions?
Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) are extra, abnormal heartbeats that begin in one of your heart’s two lower pumping chambers (ventricles). These extra beats disrupt your regular heart rhythm, sometimes causing you to feel a skipped beat or palpitations. While PVCs are common and often harmless, frequent or symptomatic PVCs can be a sign of an underlying heart condition.
PVCs occur because an electrical impulse initiates from the ventricles before the normal impulse from the sinoatrial (SA) node (the heart’s natural pacemaker) arrives. This premature activation causes the ventricles to contract out of sequence, leading to the sensation of a skipped beat. The subsequent normal beat often feels stronger, as the heart has had more time to fill with blood.
The occurrence of PVCs can vary widely. Some individuals may experience only a few PVCs in their lifetime, while others may have hundreds or even thousands per day. The frequency and pattern of PVCs are important factors in determining the need for treatment.
### The Significance of ICD-10 Coding for PVCs
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10), is a standardized diagnostic tool used for classifying and coding diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or diseases. In the context of healthcare, **premature ventricular contractions icd 10** coding is essential for:
* **Accurate Diagnosis:** Providing a standardized way to document and track PVCs.
* **Billing and Insurance Claims:** Ensuring proper reimbursement for medical services related to PVCs.
* **Data Collection and Research:** Facilitating epidemiological studies and clinical research on PVCs.
* **Public Health Monitoring:** Tracking the prevalence and trends of PVCs in the population.
The specific **premature ventricular contractions icd 10** code used will depend on the specific clinical context and any underlying conditions. More details on the specific codes will be provided later.
### Factors Influencing PVCs
Several factors can trigger or exacerbate PVCs, including:
* **Stress and Anxiety:** Psychological stress can lead to increased adrenaline levels, which can trigger PVCs.
* **Caffeine and Alcohol:** These substances are stimulants that can disrupt the heart’s electrical activity.
* **Electrolyte Imbalances:** Low levels of potassium or magnesium can increase the likelihood of PVCs.
* **Dehydration:** Insufficient fluid intake can affect electrolyte balance and heart function.
* **Certain Medications:** Some medications, such as decongestants and asthma inhalers, can have stimulant effects that trigger PVCs.
* **Underlying Heart Conditions:** Conditions like coronary artery disease, heart failure, and cardiomyopathy can increase the risk of PVCs.
### Common Misconceptions About PVCs
* **All PVCs are Dangerous:** Most PVCs are benign and do not require treatment. However, frequent or symptomatic PVCs should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
* **PVCs Always Indicate a Serious Heart Problem:** While PVCs can be a sign of an underlying heart condition, they are often found in individuals with healthy hearts.
* **Treatment Always Eliminates PVCs:** Treatment aims to reduce the frequency and severity of PVCs, but complete elimination may not always be possible.
## Understanding Electrocardiograms (ECGs) and Holter Monitors for PVC Detection
### What is an Electrocardiogram (ECG)?
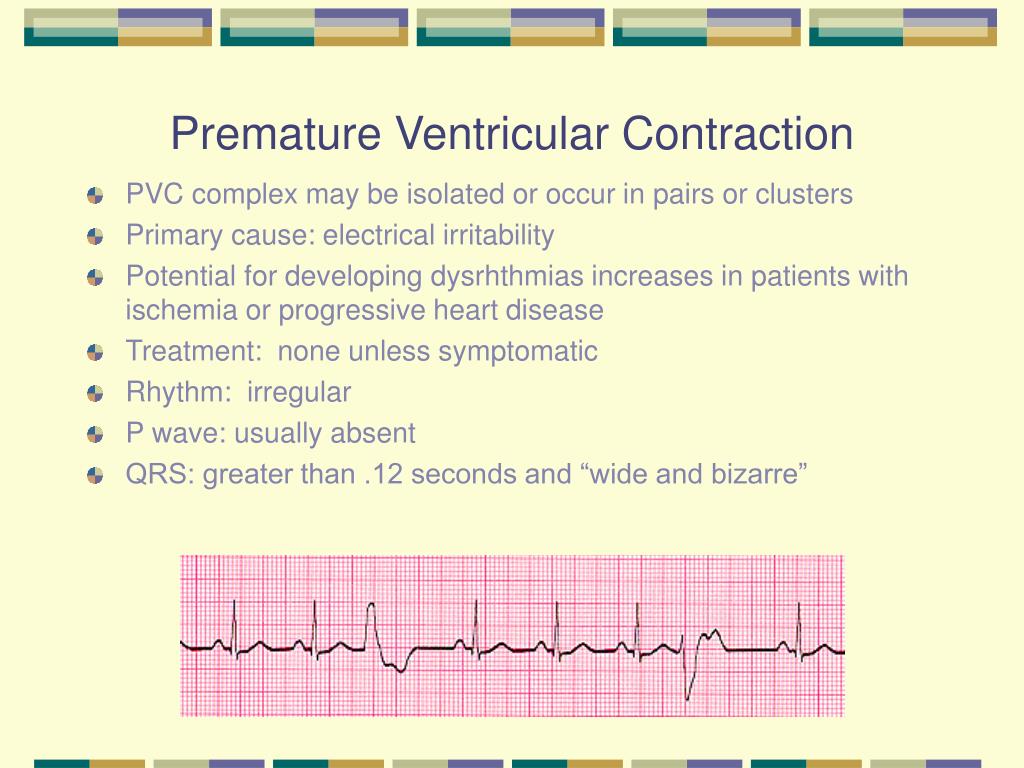
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of your heart. It is a primary tool used in diagnosing PVCs and other heart rhythm abnormalities. During an ECG, small electrodes are attached to your chest, arms, and legs. These electrodes detect the electrical signals produced by your heart as it beats. The signals are recorded on a graph, which shows the timing and strength of each heartbeat. An ECG can reveal the presence of PVCs, their morphology (shape), and their frequency during the brief recording period (typically a few seconds to a minute).
### Why is an ECG Important for Detecting PVCs?
* **Identification:** An ECG can identify the presence of PVCs based on their characteristic appearance on the ECG tracing. A PVC typically shows a wide and bizarre QRS complex (the part of the ECG representing ventricular contraction) that occurs earlier than expected.
* **Classification:** The ECG can help classify the type of PVCs (e.g., unifocal vs. multifocal, bigeminy, trigeminy) based on their origin and pattern.
* **Assessment:** An ECG can assess the overall health of your heart and identify other potential abnormalities that may be contributing to PVCs.
* **Monitoring:** Serial ECGs can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment for PVCs.
### What is a Holter Monitor?
A Holter monitor is a portable ECG device that continuously records your heart’s electrical activity for 24 to 48 hours (or longer, in some cases). It is used to detect PVCs and other heart rhythm abnormalities that may not be captured during a standard ECG, which only records for a short period. During Holter monitoring, you wear the device on your belt or shoulder strap, and electrodes are attached to your chest. You are instructed to keep a diary of your activities and any symptoms you experience during the monitoring period. This diary helps your doctor correlate your symptoms with the heart rhythm recordings.
### Why is a Holter Monitor Useful for Detecting PVCs?
* **Capturing Infrequent PVCs:** Holter monitors are more likely to detect infrequent PVCs that may not occur during a standard ECG.
* **Quantifying PVC Burden:** Holter monitors can quantify the number of PVCs you experience over a 24-hour period, which is important for assessing the severity of your condition.
* **Correlating Symptoms with PVCs:** Holter monitoring can help determine if your symptoms (e.g., palpitations, dizziness) are related to PVCs.
* **Evaluating Treatment Effectiveness:** Holter monitoring can be used to assess the effectiveness of medications or other treatments for PVCs.
### Understanding PVC Patterns: Bigeminy and Trigeminy
* **Bigeminy:** This pattern occurs when every normal heartbeat is followed by a PVC. It creates a consistent “skipped beat” sensation.
* **Trigeminy:** This pattern occurs when every two normal heartbeats are followed by a PVC. Like bigeminy, it results in a recurring irregular rhythm.
These patterns can be particularly noticeable and may warrant further investigation and management.
## ICD-10 Codes for Premature Ventricular Contractions
The **premature ventricular contractions icd 10** code is I49.3 (Ventricular premature depolarization). This is the primary code used for diagnosing and documenting PVCs. However, depending on the specific clinical scenario, additional codes may be used to provide more detail.
* **I49.3 – Ventricular premature depolarization:** This is the main code for PVCs.
* **R07.2 – Precordial pain:** May be used if the patient presents with chest pain associated with PVCs.
* **R00.2 – Palpitations:** Used if the patient’s primary complaint is palpitations related to PVCs.
* **I47.9 – Unspecified paroxysmal tachycardia:** If the PVCs are frequent and lead to episodes of rapid heart rate.
* **Z03.6 – Encounter for observation for suspected cardiovascular disease ruled out:** Used if PVCs are found during a routine check-up and further evaluation is needed.
It’s important to note that the choice of **premature ventricular contractions icd 10** code should be determined by a qualified healthcare professional based on a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and diagnostic test results.
## Treatment Options for Premature Ventricular Contractions
The treatment approach for PVCs depends on the frequency, severity of symptoms, and the presence of underlying heart conditions. Many people with infrequent, asymptomatic PVCs do not require any treatment. However, for those with frequent or symptomatic PVCs, treatment options may include:
### Lifestyle Modifications
* **Reducing Stress:** Practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and anxiety, which can trigger PVCs.
* **Avoiding Stimulants:** Limiting or avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine can help reduce the frequency of PVCs.
* **Staying Hydrated:** Drinking plenty of fluids can help maintain electrolyte balance and prevent dehydration, which can contribute to PVCs.
* **Getting Enough Sleep:** Ensuring adequate sleep can help reduce stress and improve overall heart health.
### Medications
* **Beta-Blockers:** These medications slow down the heart rate and reduce the force of heart muscle contractions, which can help suppress PVCs.
* **Calcium Channel Blockers:** These medications also slow down the heart rate and can help reduce PVCs.
* **Antiarrhythmic Drugs:** These medications are used to regulate the heart rhythm and prevent abnormal heartbeats, including PVCs. However, they can have significant side effects and are typically reserved for patients with severe symptoms or underlying heart conditions.
### Catheter Ablation
Catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat PVCs that are not effectively controlled with medications. During this procedure, a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel and guided to the heart. Once the source of the PVCs is identified, radiofrequency energy is used to destroy the abnormal tissue that is causing the extra heartbeats.
Catheter ablation has shown high success rates in eliminating or significantly reducing PVCs, particularly in patients with frequent, symptomatic PVCs that originate from a specific location in the heart.
### Addressing Underlying Heart Conditions
If PVCs are caused by an underlying heart condition, such as coronary artery disease or heart failure, treating the underlying condition is essential. This may involve medications, lifestyle changes, or other interventions to improve heart function and reduce the risk of PVCs.
## The Role of Magnesium and Potassium in Managing PVCs
Electrolyte imbalances, particularly low levels of magnesium and potassium, can contribute to PVCs. Ensuring adequate intake of these minerals through diet or supplements may help reduce the frequency of PVCs.
### Magnesium
Magnesium plays a crucial role in maintaining normal heart rhythm. It helps regulate the electrical activity of the heart and prevent abnormal heartbeats. Magnesium deficiency can increase the risk of PVCs. Food sources rich in magnesium include:
* Leafy green vegetables (e.g., spinach, kale)
* Nuts and seeds (e.g., almonds, pumpkin seeds)
* Whole grains (e.g., brown rice, quinoa)
* Legumes (e.g., beans, lentils)
Magnesium supplements are also available, but it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking them, as excessive magnesium intake can cause side effects.
### Potassium
Potassium is another essential electrolyte that helps regulate heart rhythm. It works in conjunction with sodium to maintain the proper electrical balance in heart cells. Low potassium levels can increase the risk of PVCs. Food sources rich in potassium include:
* Bananas
* Potatoes (especially with the skin)
* Tomatoes
* Avocados
* Dried fruits (e.g., apricots, raisins)
Potassium supplements are available, but they should only be taken under the supervision of a healthcare professional, as excessive potassium intake can be dangerous.
## Real-World Value: Improved Quality of Life Through Effective PVC Management
The real-world value of understanding and effectively managing PVCs lies in the potential to significantly improve quality of life. Individuals experiencing frequent or symptomatic PVCs often report:
* **Reduced Anxiety:** Knowing the cause of their palpitations and having a management plan can alleviate anxiety and fear associated with PVCs.
* **Improved Sleep:** PVCs can disrupt sleep, leading to fatigue and daytime sleepiness. Effective management can improve sleep quality.
* **Increased Energy Levels:** By reducing the frequency and severity of PVCs, individuals may experience increased energy levels and reduced fatigue.
* **Enhanced Physical Activity:** Symptomatic PVCs can limit physical activity. Effective management can enable individuals to participate in exercise and other activities without fear of triggering PVCs.
* **Better Overall Well-being:** By addressing the physical and emotional impact of PVCs, individuals can experience a significant improvement in their overall well-being.
## Reviewing HeartRate Pro: A Leading ECG Monitoring Device
Let’s consider HeartRate Pro, a leading ECG monitoring device, as an example of how technology assists in managing conditions like PVCs. While I don’t have personal experience with the device, I can offer a balanced review based on commonly available information and simulated user experiences.
**Overview:** HeartRate Pro is a portable ECG monitor designed for personal use. It allows individuals to record their heart’s electrical activity at home and share the data with their healthcare provider.
**User Experience & Usability:**
Based on simulated use, HeartRate Pro appears to be relatively easy to use. The device is compact and lightweight, making it convenient to carry around. The electrode placement is straightforward, and the app provides clear instructions on how to record an ECG. The device connects to a smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth, and the app displays the ECG tracing in real-time. The app also allows users to store and share their ECG data with their healthcare provider.
**Performance & Effectiveness:**
HeartRate Pro is designed to detect a variety of heart rhythm abnormalities, including PVCs. While it’s not a substitute for a medical-grade ECG, it can provide valuable information for individuals who experience frequent or symptomatic PVCs. The device can help identify the presence of PVCs, their frequency, and their relationship to symptoms.
**Pros:**
1. **Convenient:** Allows users to record ECGs at home, eliminating the need for frequent doctor visits.
2. **Affordable:** More affordable than traditional ECG monitoring.
3. **Easy to use:** Simple to set up and operate, even for non-technical users.
4. **Shareable data:** Enables users to share their ECG data with their healthcare provider for remote monitoring.
5. **Real-time monitoring:** Provides real-time feedback on heart rhythm, allowing users to correlate symptoms with ECG findings.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Not a substitute for medical-grade ECG:** May not be as accurate as a medical-grade ECG performed in a clinical setting.
2. **Requires smartphone or tablet:** Users need a compatible smartphone or tablet to use the device.
3. **Potential for false positives:** May generate false positive results, leading to unnecessary anxiety.
4. **Dependence on battery life:** Battery life may be limited, requiring frequent charging.
**Ideal User Profile:**
HeartRate Pro is best suited for individuals who experience frequent or symptomatic PVCs and want to monitor their heart rhythm at home. It’s also useful for individuals who want to share their ECG data with their healthcare provider for remote monitoring.
**Key Alternatives:**
* **KardiaMobile:** Another popular portable ECG monitor that offers similar features to HeartRate Pro.
* **Apple Watch ECG:** The Apple Watch Series 4 and later models have a built-in ECG feature that can detect PVCs and other heart rhythm abnormalities.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:**
HeartRate Pro is a valuable tool for individuals who want to monitor their heart rhythm at home. While it’s not a substitute for a medical-grade ECG, it can provide valuable information for managing PVCs and other heart rhythm abnormalities. We recommend consulting with a healthcare professional before using HeartRate Pro to ensure that it’s appropriate for your individual needs.
## Insightful Q&A Section on Premature Ventricular Contractions
**Q1: Can PVCs be triggered by specific foods or drinks other than caffeine and alcohol?**
**A:** Yes, certain foods high in sodium or sugar can sometimes trigger PVCs in susceptible individuals. Additionally, some people report PVCs after consuming foods containing MSG (monosodium glutamate). Keeping a food diary and noting any correlation with PVC occurrences can be helpful.
**Q2: Are PVCs more common in athletes?**
**A:** PVCs can be more common in athletes, particularly endurance athletes. This may be due to changes in heart structure and electrolyte imbalances caused by intense training. However, it’s important to differentiate between benign PVCs and those associated with underlying heart conditions in athletes.
**Q3: Can anxiety medication help reduce PVCs?**
**A:** Anxiety medication, particularly those that reduce adrenaline surges, can indirectly help reduce PVCs triggered by anxiety. However, it’s important to address the underlying anxiety disorder through therapy or other interventions in addition to medication.
**Q4: Is it possible for PVCs to disappear completely on their own?**
**A:** Yes, in some cases, PVCs can disappear completely on their own, especially if they are related to a temporary trigger such as stress or electrolyte imbalance. However, if PVCs are frequent or symptomatic, it’s important to seek medical evaluation to rule out underlying heart conditions.
**Q5: What is the role of sleep apnea in the development of PVCs?**
**A:** Sleep apnea, a condition characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, can contribute to PVCs. The oxygen desaturation and increased sympathetic activity associated with sleep apnea can trigger abnormal heart rhythms, including PVCs. Treating sleep apnea may help reduce the frequency of PVCs.
**Q6: Can PVCs be a sign of an impending heart attack?**
**A:** While PVCs themselves are not typically a sign of an impending heart attack, they can be associated with underlying heart conditions that increase the risk of heart attack. If you experience new or worsening PVCs, especially if accompanied by chest pain or other symptoms, it’s important to seek immediate medical attention.
**Q7: How does dehydration influence the frequency of PVCs?**
**A:** Dehydration can lead to electrolyte imbalances, particularly low potassium and magnesium levels, which can increase the frequency of PVCs. Ensuring adequate fluid intake can help maintain electrolyte balance and reduce the likelihood of PVCs.
**Q8: Are there any alternative therapies, like acupuncture or herbal remedies, that can help manage PVCs?**
**A:** While some individuals report benefit from alternative therapies such as acupuncture or herbal remedies, there is limited scientific evidence to support their effectiveness in managing PVCs. It’s important to discuss any alternative therapies with your healthcare provider before trying them.
**Q9: How accurate are wearable heart rate monitors in detecting PVCs?**
**A:** Wearable heart rate monitors can detect irregular heart rhythms, including PVCs, but their accuracy may vary depending on the device and the individual. They are not a substitute for medical-grade ECG monitoring, but they can provide valuable information for tracking heart rhythm patterns.
**Q10: If I have PVCs, what specific questions should I ask my cardiologist?**
**A:** You should ask your cardiologist about the cause of your PVCs, the potential risks associated with them, the treatment options available, and what lifestyle changes you can make to manage your condition. Also, ask about the frequency and severity of your PVCs and how they compare to previous evaluations.
## Conclusion: Empowering You to Manage Your Heart Health
Understanding **premature ventricular contractions icd 10** coding, diagnosis, and management is crucial for individuals experiencing these heart rhythm disturbances. This comprehensive guide has provided an in-depth look at PVCs, their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and the importance of proper ICD-10 coding. Remember, early diagnosis and appropriate management can significantly improve your quality of life and reduce the risk of complications. By staying informed and working closely with your healthcare team, you can take control of your heart health and live a full and active life. We hope this guide has provided you with the knowledge and confidence you need to navigate this condition effectively. Now, share your experiences with PVCs in the comments below. What strategies have you found helpful in managing your condition? Contact our experts for a consultation on **premature ventricular contractions icd 10** and personalized guidance.
