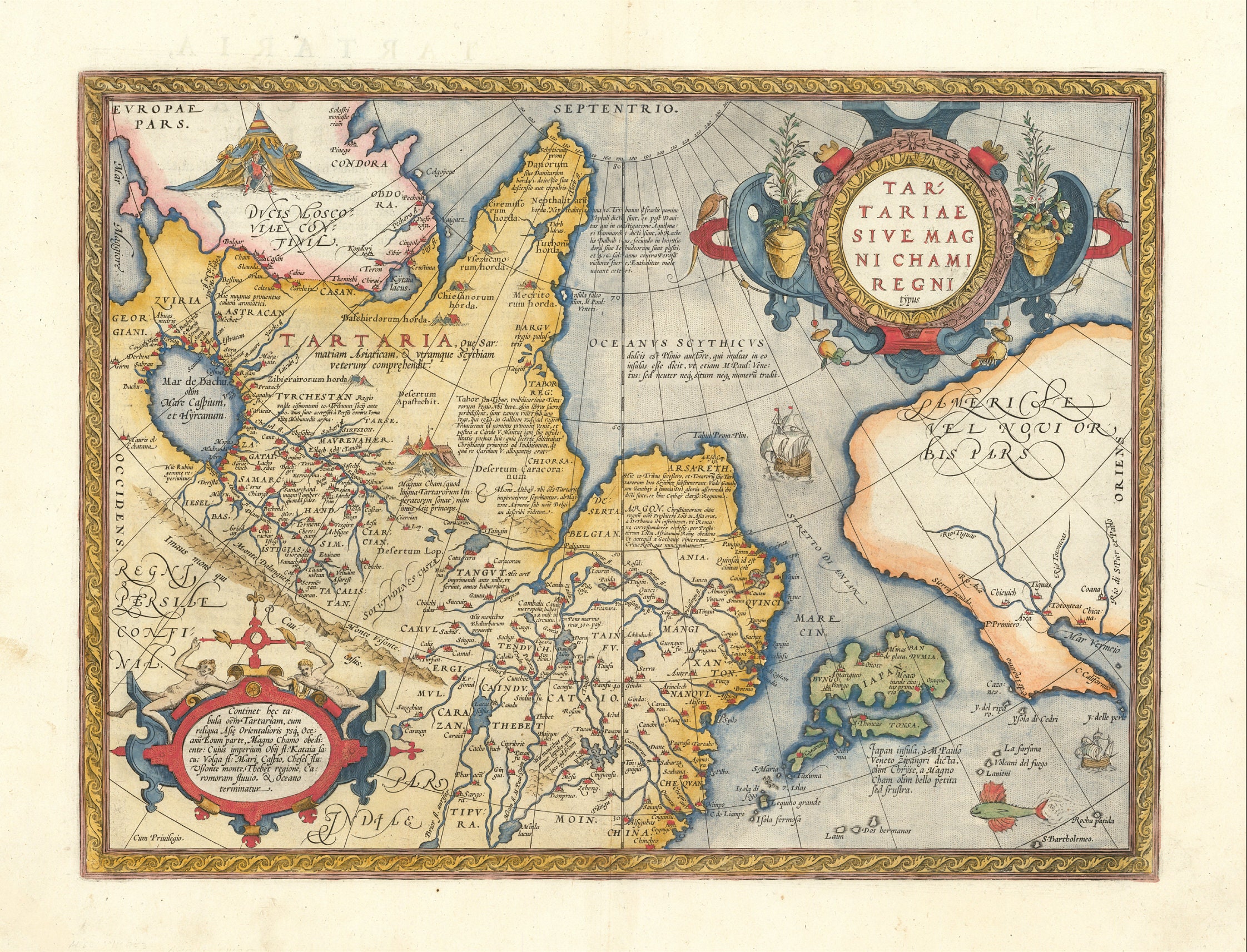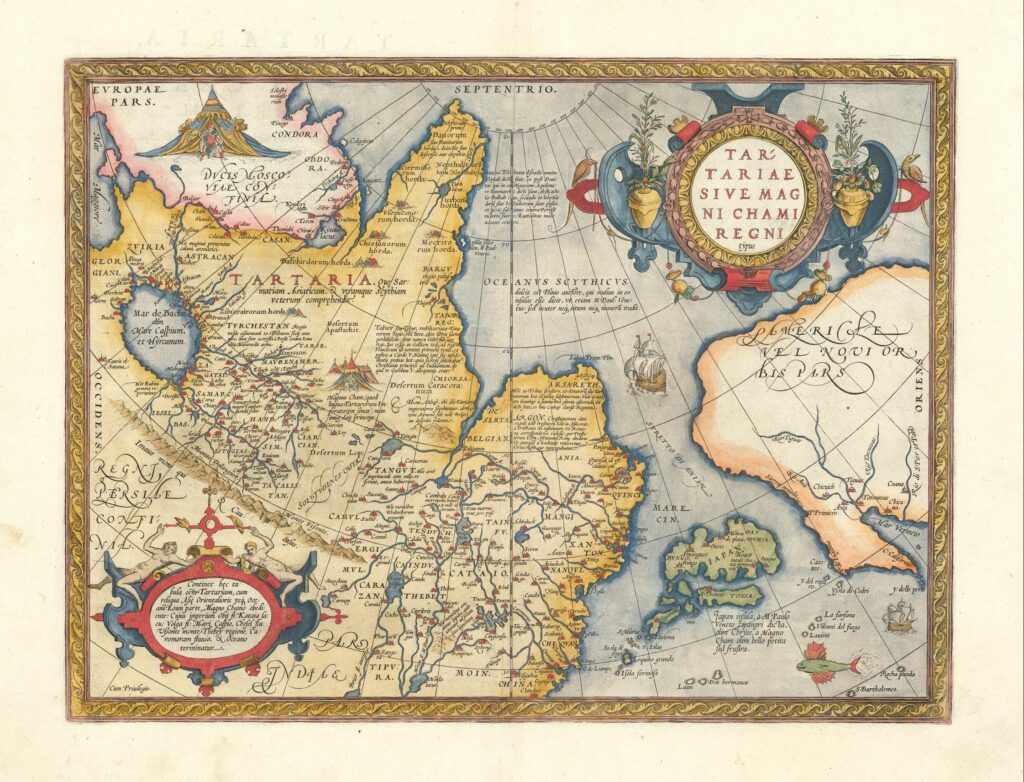
Tartarian Map: Unveiling the Mysteries of a Lost Civilization
Are you intrigued by historical enigmas and alternative theories? The “Tartarian Map” has captivated researchers, historians, and curious minds alike. This article delves into the depths of this fascinating subject, separating fact from fiction and providing you with a comprehensive understanding of what the Tartarian Map represents, its alleged connections to a lost civilization, and its place in historical discourse. We aim to provide a definitive resource, drawing upon available evidence and expert perspectives to present a balanced and insightful exploration of this intriguing topic.
What is the Tartarian Map? Exploring the Historical Context
The term “Tartarian Map” often refers to maps depicting a vast, powerful empire called “Tartary” or “Great Tartary” that purportedly existed in Central Asia and beyond. These maps, primarily dating from the 16th to 19th centuries, show Tartary as a significant geographical entity, sometimes encompassing territories from Eastern Europe to the Pacific Ocean. However, the nature and existence of Tartary as a unified empire are heavily debated and remain a subject of historical inquiry.
The maps themselves are not necessarily a single, definitive “Tartarian Map,” but rather a collection of cartographic representations created by various European and Asian mapmakers over several centuries. These maps reflect the evolving geographical knowledge and political perceptions of the time. The variations and inconsistencies between different maps contribute to the ongoing mystery surrounding Tartary.
It’s crucial to understand that these maps were created during a period of exploration, colonization, and geopolitical maneuvering. European powers were expanding their influence across the globe, and their cartographic representations often reflected their own agendas and limited understanding of distant lands. Therefore, interpreting these maps requires a critical eye and an awareness of the historical context in which they were produced.
The Evolution of Cartographic Knowledge
Cartography has evolved significantly throughout history. Early maps were often based on limited exploration, anecdotal accounts, and religious or philosophical beliefs. As exploration and scientific methods advanced, maps became more accurate and detailed. Understanding this evolution is essential for interpreting historical maps, including those depicting Tartary.
Tartary in Historical Records
References to Tartary can be found in various historical sources, including travelogues, chronicles, and diplomatic documents. These sources offer glimpses into the interactions between Europeans and the peoples of Central Asia. However, the accounts are often fragmented, contradictory, and subject to bias. Piecing together a coherent picture of Tartary from these sources remains a challenge.
Debunking and Exploring Tartarian Theories: Separating Fact from Fiction
In recent years, the concept of Tartary has gained traction within alternative history circles. Some theories propose that Tartary was a highly advanced, technologically sophisticated civilization that was deliberately erased from mainstream history. These theories often suggest that Tartary possessed advanced knowledge of free energy, architecture, and other technologies that have been suppressed by a global conspiracy. However, these claims lack credible evidence and are often based on misinterpretations of historical sources and architectural styles.
It’s important to approach these theories with a critical and discerning mind. While exploring alternative perspectives can be intellectually stimulating, it’s crucial to rely on verifiable evidence and sound reasoning. Extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence, and the claims surrounding Tartary often fall short of this standard.
The Mud Flood Theory and Tartarian Architecture
One popular theory associated with Tartary is the “mud flood theory.” This theory suggests that a cataclysmic event, such as a massive mud flood, buried much of Tartarian civilization, leaving behind only remnants of its grand architecture. Proponents of this theory often point to buildings with partially buried windows or doors as evidence of the mud flood. However, these features can often be explained by natural processes, such as soil erosion, subsidence, or deliberate architectural design.
Furthermore, the architectural styles attributed to Tartary are often found in various parts of the world and reflect the influence of different cultures and historical periods. Attributing these styles solely to Tartary ignores the complex interplay of architectural influences and the diversity of human creativity.
The Conspiracy Angle: Was Tartary Erased from History?
Another common claim is that Tartary was deliberately erased from history by a global conspiracy. This theory suggests that powerful forces sought to suppress knowledge of Tartary’s advanced civilization and its potential to challenge the established order. However, there is no credible evidence to support this claim. The historical record is complex and often incomplete, but there is no indication of a systematic effort to erase Tartary from existence.
While it’s true that some historical narratives may be biased or incomplete, attributing this to a deliberate conspiracy is a leap of faith. It’s more likely that the limited understanding of Tartary reflects the challenges of historical research and the incomplete nature of the historical record.
The Power of Maps: How Cartography Shapes Our Understanding
Maps are not simply neutral representations of geographical reality; they are powerful tools that shape our understanding of the world. Maps reflect the values, beliefs, and agendas of their creators. They can be used to promote political ideologies, justify territorial claims, and reinforce social hierarchies. Understanding the power of maps is crucial for interpreting historical cartography, including maps depicting Tartary.
Historical maps often reflect the limited geographical knowledge of the time. Mapmakers may have relied on anecdotal accounts, incomplete surveys, or religious or philosophical beliefs to fill in the gaps in their knowledge. As a result, historical maps may contain inaccuracies, distortions, and omissions.
The Mercator Projection and Its Impact
The Mercator projection, a cylindrical map projection developed in the 16th century, is a prime example of how map projections can distort our perception of the world. While the Mercator projection is useful for navigation, it significantly distorts the size and shape of landmasses, particularly those located at higher latitudes. This distortion can lead to a Eurocentric view of the world, where Europe appears larger and more important than it actually is.
The Political Cartography of Tartary
Maps depicting Tartary often reflect the political dynamics of the time. European powers were competing for influence in Central Asia, and their cartographic representations often reflected their own ambitions and rivalries. Maps may have exaggerated the size and power of Tartary to justify military expeditions or diplomatic negotiations. Conversely, maps may have downplayed the importance of Tartary to diminish its perceived threat.
The Role of Tartary in Modern Culture: From Historical Mystery to Internet Phenomenon
The concept of Tartary has experienced a resurgence in popularity in recent years, fueled by the internet and the spread of alternative theories. Online forums, social media groups, and YouTube channels have become platforms for discussing and debating the existence of Tartary and its alleged advanced civilization. This online community has contributed to the creation of a vibrant and often speculative narrative surrounding Tartary.
While the online discussion of Tartary can be intellectually stimulating, it’s important to approach these discussions with a critical and discerning mind. Not all information shared online is accurate or reliable. It’s crucial to verify claims, consult credible sources, and avoid falling prey to misinformation and conspiracy theories.
Tartary as a Symbol of Alternative History
For many, Tartary represents a symbol of alternative history, a challenge to the mainstream narrative. It embodies the desire to question established assumptions, explore hidden histories, and uncover forgotten truths. While this spirit of inquiry is commendable, it’s important to ensure that the pursuit of alternative history is grounded in evidence and reason.
The Importance of Historical Literacy
The ongoing debate surrounding Tartary highlights the importance of historical literacy. Understanding the historical context, the methods of historical research, and the limitations of historical evidence is crucial for navigating complex historical narratives. By developing our historical literacy, we can better evaluate claims, distinguish fact from fiction, and appreciate the richness and complexity of the past.
Expert Explanation: Analyzing the Evidence for and Against Tartary
To gain a deeper understanding of the Tartarian Map and the theories surrounding it, let’s analyze the available evidence from an expert viewpoint. The key lies in critically evaluating historical maps, texts, and architectural styles often associated with the alleged Tartarian empire.
Historical maps, while visually compelling, must be interpreted with caution. As mentioned earlier, these maps were products of their time, influenced by limited geographical knowledge, political agendas, and varying levels of accuracy. The depiction of “Tartary” on these maps doesn’t automatically confirm the existence of a unified, advanced empire. It’s more likely a reflection of European perceptions of Central Asia and its diverse nomadic peoples.
Similarly, historical texts mentioning “Tartary” often refer to the vast steppes of Central Asia and its inhabitants, who were known for their nomadic lifestyle and military prowess. These texts don’t necessarily describe a single, coherent civilization with advanced technology. The term “Tartar” was often used broadly to refer to various nomadic groups, without necessarily implying a shared culture or political structure.
Architectural styles attributed to Tartary, such as grand buildings with intricate details and partially buried structures, can be found in various parts of the world and reflect the influence of different cultures and historical periods. Attributing these styles solely to Tartary ignores the complex interplay of architectural influences and the diversity of human creativity. The “mud flood theory,” often used to explain the partially buried structures, lacks scientific evidence and can often be explained by natural processes such as soil erosion and subsidence.
Detailed Feature Analysis: Examining Key Claims Associated with Tartary
Let’s delve into specific claims often made by proponents of Tartarian theories and analyze them in detail:
1. **Advanced Technology:** Claim: Tartary possessed advanced technology, such as free energy devices and sophisticated architectural techniques. Analysis: There is no credible evidence to support this claim. The architectural styles attributed to Tartary are consistent with the technology and knowledge of the time. The concept of “free energy” is often based on pseudoscientific ideas and lacks scientific validation.
2. **Global Empire:** Claim: Tartary was a vast, global empire that controlled much of the world. Analysis: Historical maps depict Tartary as a significant geographical entity, but this doesn’t necessarily imply political control. The term “Tartary” was often used to refer to a loosely defined region inhabited by various nomadic groups. There is no evidence of a centralized government or a unified political structure.
3. **Eradication from History:** Claim: Tartary was deliberately erased from history by a global conspiracy. Analysis: There is no credible evidence to support this claim. The historical record is complex and often incomplete, but there is no indication of a systematic effort to erase Tartary from existence. The limited understanding of Tartary likely reflects the challenges of historical research and the incomplete nature of the historical record.
4. **Mud Flood Cataclysm:** Claim: A massive mud flood destroyed much of Tartarian civilization. Analysis: The “mud flood theory” lacks scientific evidence. The architectural features often attributed to the mud flood can often be explained by natural processes such as soil erosion and subsidence.
5. **Unique Architectural Style:** Claim: Tartary had a unique and distinct architectural style. Analysis: The architectural styles attributed to Tartary are found in various parts of the world and reflect the influence of different cultures and historical periods. There is no evidence of a unique architectural style that can be definitively attributed to Tartary.
6. **Advanced Knowledge of Energy:** Claim: Tartarians possessed advanced knowledge of energy and used it in their architecture. Analysis: This claim is often linked to the idea of free energy and lacks scientific support. The architectural features attributed to this knowledge can be explained by conventional engineering principles.
7. **Connection to Ancient Civilizations:** Claim: Tartary was connected to other ancient civilizations like Atlantis or Lemuria. Analysis: These connections are purely speculative and lack any historical or scientific basis.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value: Understanding the Appeal of Tartarian Theories
While the historical claims surrounding Tartary may lack evidence, understanding the *appeal* of these theories provides valuable insight into human psychology and the desire for alternative narratives. The advantages, benefits, and real-world value, though often perceived rather than actual, can be broken down as follows:
* **Challenging the Status Quo:** Tartarian theories offer a way to question established historical narratives and challenge the authority of mainstream institutions. This can be empowering for individuals who feel marginalized or distrustful of traditional sources of information. Users gain a sense of agency by rejecting the conventional and embracing the unconventional.
* **Sense of Discovery:** Exploring alternative histories can create a sense of excitement and discovery. The idea that there are hidden truths waiting to be uncovered can be highly motivating. It satisfies a human desire to learn and explore new frontiers, even if those frontiers are based on speculation.
* **Community and Belonging:** Engaging with Tartarian theories often involves joining online communities and connecting with like-minded individuals. This can provide a sense of belonging and shared purpose. It creates a social network where people can exchange ideas, share information, and support each other.
* **Intellectual Stimulation:** Even if the claims are ultimately unfounded, exploring Tartarian theories can be intellectually stimulating. It requires critical thinking, research, and the ability to connect disparate pieces of information. This process can enhance cognitive skills and broaden one’s understanding of history and culture.
* **Reinterpreting the Past:** Tartarian theories offer a new lens through which to view historical events and architectural styles. This can lead to fresh perspectives and a deeper appreciation for the complexity of the past. Even if the interpretations are not historically accurate, they can still be thought-provoking and inspiring.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review: Evaluating the Merits and Limitations of Tartarian Research
Let’s provide a balanced and in-depth review of the concept of Tartary, acknowledging its appeal while also highlighting its limitations:
* **User Experience & Usability (of Tartarian Theories):** Engaging with Tartarian theories is often a solitary pursuit, involving online research and personal reflection. The information can be scattered and inconsistent, requiring significant effort to sift through. The lack of reliable sources and the prevalence of misinformation can make the process frustrating.
* **Performance & Effectiveness (of Tartarian Theories):** Tartarian theories, by their nature, are not designed to be “effective” in a practical sense. They are primarily aimed at providing alternative explanations for historical phenomena. However, they often fail to provide verifiable evidence or logical reasoning to support their claims.
* **Pros:**
* Encourages critical thinking and questioning of established narratives.
* Promotes historical literacy and the exploration of diverse perspectives.
* Fosters a sense of community and belonging among like-minded individuals.
* Provides intellectual stimulation and a fresh lens through which to view the past.
* Highlights the importance of evidence-based reasoning and source evaluation.
* **Cons/Limitations:**
* Often relies on misinformation, speculation, and conspiracy theories.
* Lacks credible evidence to support its central claims.
* Can lead to misinterpretations of historical events and architectural styles.
* May promote distrust of mainstream institutions and established knowledge.
* **Ideal User Profile:** Individuals with a strong interest in alternative history, a willingness to question established narratives, and a commitment to critical thinking and evidence-based reasoning.
* **Key Alternatives:** Mainstream historical research, academic studies of cartography, and critical analysis of conspiracy theories.
* **Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:** While the concept of Tartary can be intellectually stimulating and encourage critical thinking, it’s crucial to approach it with a discerning mind and a commitment to evidence-based reasoning. The claims surrounding Tartary often lack credible evidence and are based on misinterpretations of historical sources and architectural styles. It’s important to consult reliable sources, verify claims, and avoid falling prey to misinformation and conspiracy theories. I recommend approaching the topic as a thought experiment rather than historical fact.
Insightful Q&A Section: Addressing Common Questions and Concerns
Here are 10 insightful questions related to the Tartarian Map and its associated theories, along with expert answers:
1. **Q: What is the most compelling evidence supporting the existence of Tartary as an advanced civilization?**
* A: There is no compelling evidence to support the existence of Tartary as an advanced civilization. Claims of advanced technology and a global empire are based on misinterpretations of historical sources and architectural styles.
2. **Q: How can I distinguish between credible and unreliable sources of information about Tartary?**
* A: Consult academic sources, historical archives, and reputable websites. Be wary of websites that promote conspiracy theories or lack verifiable evidence. Always cross-reference information and evaluate the credibility of the source.
3. **Q: What are some common misconceptions about Tartarian architecture?**
* A: A common misconception is that Tartarian architecture is unique and distinct. In reality, the architectural styles attributed to Tartary are found in various parts of the world and reflect the influence of different cultures and historical periods.
4. **Q: Is there any scientific evidence to support the mud flood theory?**
* A: No, there is no scientific evidence to support the mud flood theory. The architectural features often attributed to the mud flood can often be explained by natural processes such as soil erosion and subsidence.
5. **Q: How did the term “Tartary” originate?**
* A: The term “Tartary” likely originated from the Mongol invasions of Europe in the 13th century. Europeans used the term to refer to the vast steppes of Central Asia and its inhabitants.
6. **Q: What role did maps play in shaping European perceptions of Tartary?**
* A: Maps reflected the limited geographical knowledge, political agendas, and varying levels of accuracy of the time. The depiction of “Tartary” on these maps doesn’t automatically confirm the existence of a unified, advanced empire.
7. **Q: Why has the concept of Tartary gained popularity in recent years?**
* A: The internet and the spread of alternative theories have fueled the resurgence of Tartary. The concept offers a way to question established narratives and challenge the authority of mainstream institutions.
8. **Q: What are some potential dangers of engaging with Tartarian theories?**
* A: Engaging with Tartarian theories can lead to misinformation, speculation, and distrust of mainstream institutions. It’s important to approach these theories with a critical and discerning mind.
9. **Q: How can I promote historical literacy and critical thinking when discussing Tartary?**
* A: Encourage the use of reliable sources, the evaluation of evidence, and the consideration of alternative perspectives. Emphasize the importance of historical context and the limitations of historical evidence.
10. **Q: What is the most important takeaway from the study of the Tartarian Map and its associated theories?**
* A: The most important takeaway is the need for critical thinking, evidence-based reasoning, and a healthy skepticism when evaluating historical claims. The Tartarian Map serves as a reminder that history is complex and often subject to interpretation.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, the “Tartarian Map” and the theories surrounding it present a fascinating case study in the power of maps, the appeal of alternative histories, and the importance of critical thinking. While the claims of an advanced Tartarian civilization lack credible evidence, the ongoing debate highlights the human desire to question established narratives and explore hidden truths. Remember to approach these discussions with a discerning mind, a commitment to evidence-based reasoning, and a healthy dose of skepticism.
We encourage you to continue exploring this topic, but always prioritize reliable sources and critical evaluation. Share your thoughts and perspectives in the comments below, and let’s continue the conversation in a constructive and informed manner. Explore our other articles on historical cartography and alternative history for more insights into the complexities of the past.