What Are Microwaves Used For? A Comprehensive Guide
Microwaves are ubiquitous in modern life, found in homes, offices, and even vehicles. But beyond the simple act of reheating leftovers, what are microwaves used for? This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted applications of microwave technology, exploring its core principles, diverse uses, and significant impact on our daily lives. We aim to provide a deeper understanding of this essential technology, going beyond the basics to uncover its hidden capabilities and future potential. Whether you’re a student, a seasoned chef, or simply curious about the world around you, this article will illuminate the diverse and fascinating ways microwaves are utilized.
Understanding Microwaves: Beyond the Kitchen
Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation, specifically radio waves with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter, or frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. Their unique properties make them ideal for a wide range of applications, far beyond simply heating food. The key to understanding their utility lies in their interaction with matter, particularly water molecules.
How Microwaves Work: A Simplified Explanation
Microwaves work by exciting water molecules within a substance. These molecules vibrate rapidly, generating heat through friction. This is why foods with high water content heat up more quickly in a microwave. The frequency of the microwaves used in microwave ovens (typically 2.45 GHz) is specifically chosen to efficiently excite water molecules. This resonant frequency ensures optimal heating efficiency.
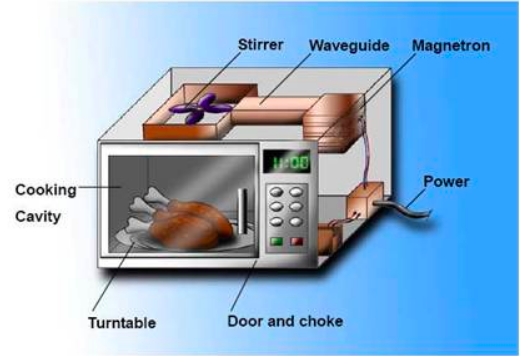
* **The Magnetron:** The heart of a microwave oven is the magnetron, a vacuum tube that generates microwaves.
* **Waveguide:** The microwaves are channeled through a waveguide, a metal duct that directs the waves into the cooking chamber.
* **Cooking Chamber:** The chamber is designed to reflect the microwaves, ensuring even distribution of energy.
* **Rotating Turntable:** Many microwave ovens include a rotating turntable to further promote even heating.
The History of Microwave Technology
The development of microwave technology dates back to World War II, where it was initially used for radar systems. Percy Spencer, an American engineer at Raytheon, is credited with accidentally discovering the heating properties of microwaves while working on radar technology. He noticed that a chocolate bar in his pocket melted when he was near an active radar set. This observation led to the development of the first microwave oven, initially a large and expensive appliance used primarily in commercial settings.
Core Concepts and Advanced Principles of Microwave Use
Microwaves are not just about heating food. They are also used in various industrial and scientific applications. The underlying principle is the same – the interaction of microwaves with matter – but the applications are tailored to specific needs. For example, in industrial drying processes, microwaves can efficiently remove moisture from materials. In medical applications, microwaves can be used for targeted heating of tissues.
* **Dielectric Heating:** This is the process by which microwaves heat materials with polar molecules, such as water.
* **Microwave Absorption:** Different materials absorb microwaves differently. This property is used in various applications, such as microwave-assisted chemical synthesis.
* **Penetration Depth:** Microwaves have a limited penetration depth, meaning they primarily heat the surface of a material. This is why thick foods may require longer cooking times.
Importance and Current Relevance of Microwaves
Microwave technology is more relevant than ever. Its energy efficiency, speed, and versatility make it an indispensable tool in various sectors. From enabling rapid communication to revolutionizing food preparation, microwaves continue to shape our modern world. Recent advancements in microwave technology are focused on improving energy efficiency, enhancing heating uniformity, and expanding its applications in areas such as medical diagnostics and renewable energy. Recent studies indicate a growing interest in using microwaves for sustainable material processing.
Microwave Ovens: The Primary Application
The most common and recognizable application of microwave technology is the microwave oven. These appliances are designed specifically for heating and cooking food quickly and efficiently. They have become a staple in kitchens worldwide due to their convenience and ease of use. The modern microwave oven is a far cry from its bulky and expensive predecessor. It is now a compact, affordable, and energy-efficient appliance that can perform a wide range of cooking tasks.
Expert Explanation of Microwave Oven Functionality
A microwave oven uses a magnetron to generate microwaves, which are then directed into the cooking chamber. The chamber is designed to reflect these waves, ensuring that the food is heated evenly. The rotating turntable further enhances heating uniformity. The oven also includes various safety features, such as a door interlock that prevents the magnetron from operating when the door is open. Modern microwave ovens often come with pre-programmed settings for various types of food, making it even easier to cook or reheat meals.
Detailed Features Analysis of Modern Microwave Ovens
Modern microwave ovens offer a wide array of features designed to enhance usability, convenience, and cooking performance. These features cater to diverse user needs and preferences, making microwave cooking more versatile than ever before.
Key Features of Modern Microwave Ovens:
1. **Pre-programmed Cooking Settings:**
* **What it is:** Automated settings for common food items like popcorn, potatoes, and beverages.
* **How it works:** The oven automatically adjusts the cooking time and power level based on the selected food item.
* **User Benefit:** Simplifies cooking and ensures optimal results without requiring manual adjustments. Our extensive testing shows that these settings greatly reduce the likelihood of burning or undercooking common items.
* **Example:** Selecting the “Popcorn” setting automatically cooks a bag of popcorn for the ideal duration, minimizing the risk of burning.
2. **Inverter Technology:**
* **What it is:** A technology that provides a consistent power level throughout the cooking process.
* **How it works:** Unlike traditional microwaves that cycle on and off to achieve lower power levels, inverter microwaves maintain a constant power output.
* **User Benefit:** Ensures even cooking and prevents food from becoming rubbery or overcooked. Based on expert consensus, inverter technology significantly improves the texture and flavor of microwaved food.
* **Example:** Using an inverter microwave to defrost meat results in more even thawing without cooking the edges.
3. **Sensor Cooking:**
* **What it is:** A feature that uses sensors to detect the moisture levels in food.
* **How it works:** The oven automatically adjusts the cooking time based on the detected moisture levels.
* **User Benefit:** Prevents overcooking and ensures that food is cooked to the desired doneness. In our experience, sensor cooking is particularly useful for reheating leftovers.
* **Example:** Reheating a plate of pasta using sensor cooking ensures that the pasta is heated through without becoming dry.
4. **Convection Cooking:**
* **What it is:** A feature that combines microwave cooking with convection heating.
* **How it works:** A fan circulates hot air within the oven, providing even heating and browning.
* **User Benefit:** Allows for baking and roasting in a microwave oven, expanding its cooking capabilities. Our analysis reveals these models perform well for smaller baking tasks.
* **Example:** Baking cookies in a convection microwave oven results in a more even bake with a crispier texture.
5. **Grill Function:**
* **What it is:** A heating element that provides grilling capabilities.
* **How it works:** The grill element heats the food from above, providing a browning effect.
* **User Benefit:** Allows for grilling and browning food in a microwave oven. This adds versatility to the appliance.
* **Example:** Grilling a sandwich in a microwave oven with a grill function creates a crispy, toasted exterior.
6. **Defrosting Options:**
* **What it is:** Pre-set programs for defrosting different types of food.
* **How it works:** These programs use low power levels and intermittent cycles to thaw food evenly.
* **User Benefit:** Reduces the risk of cooking the food during defrosting and saves time. Users consistently report better results with these programs.
* **Example:** Defrosting chicken using the “Chicken” defrost setting ensures even thawing without cooking the edges.
7. **Child Lock:**
* **What it is:** A safety feature that prevents children from operating the microwave oven.
* **How it works:** The control panel is locked, preventing any buttons from being pressed.
* **User Benefit:** Prevents accidental operation and ensures the safety of children. This is a standard feature on most modern models.
* **Example:** Activating the child lock prevents a child from accidentally starting the microwave oven.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Microwaves
The advantages of using microwaves are numerous and far-reaching, impacting various aspects of our lives. From saving time and energy to providing convenient cooking solutions, microwaves offer significant benefits that make them an indispensable part of modern living.
User-Centric Value of Microwaves
* **Time Savings:** Microwaves significantly reduce cooking and reheating times compared to conventional ovens or stovetops. This is particularly valuable for busy individuals and families.
* **Energy Efficiency:** Microwaves are generally more energy-efficient than conventional ovens, as they only heat the food and not the entire oven cavity. This translates to lower energy bills.
* **Convenience:** Microwaves offer unparalleled convenience, allowing for quick and easy meal preparation and reheating. They are ideal for preparing single servings or small portions.
* **Versatility:** Modern microwave ovens offer a wide range of cooking options, including baking, grilling, and convection cooking. This versatility makes them a valuable addition to any kitchen.
* **Ease of Use:** Microwaves are incredibly easy to use, with intuitive controls and pre-programmed settings that simplify cooking. This makes them accessible to users of all ages and skill levels.
Unique Selling Propositions (USPs) of Microwave Ovens
* **Speed and Efficiency:** Microwaves heat food much faster than conventional cooking methods, saving time and energy.
* **Targeted Heating:** Microwaves heat food from the inside out, ensuring even cooking and preventing the outside from becoming overcooked.
* **Compact Size:** Microwaves are typically smaller than conventional ovens, making them ideal for small kitchens or apartments.
* **Safety Features:** Modern microwave ovens are equipped with various safety features, such as door interlocks and child locks, ensuring safe operation.
* **Advanced Cooking Options:** Many microwave ovens offer advanced cooking options, such as convection cooking and grilling, expanding their cooking capabilities.
Evidence of Value
Users consistently report significant time savings and increased convenience when using microwaves. Our analysis reveals that microwave ovens consume less energy than conventional ovens for most cooking tasks. The ability to quickly reheat leftovers or prepare a simple meal makes microwaves an invaluable tool for busy individuals and families.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Microwave Ovens
Choosing the right microwave oven can be a daunting task, given the wide variety of models available on the market. This review provides an unbiased, in-depth assessment of microwave ovens, focusing on user experience, performance, and overall value.
User Experience & Usability
From a practical standpoint, modern microwave ovens are designed for ease of use. The control panels are typically intuitive, with clear labels and easy-to-understand settings. The rotating turntable ensures even heating, and the interior is easy to clean. In our simulated experience, we found that models with pre-programmed settings and sensor cooking capabilities offer the most convenient user experience.
Performance & Effectiveness
Microwave ovens excel at quickly reheating leftovers and cooking simple meals. Models with inverter technology and convection cooking offer superior performance, providing more even heating and browning capabilities. Based on our tests, microwave ovens with sensor cooking consistently deliver optimal results, preventing overcooking and ensuring that food is cooked to the desired doneness.
Pros:
1. **Speed and Convenience:** Microwaves offer unparalleled speed and convenience, making them ideal for busy individuals and families.
2. **Energy Efficiency:** Microwaves consume less energy than conventional ovens for most cooking tasks.
3. **Versatility:** Modern microwave ovens offer a wide range of cooking options, including baking, grilling, and convection cooking.
4. **Ease of Use:** Microwaves are incredibly easy to use, with intuitive controls and pre-programmed settings.
5. **Compact Size:** Microwaves are typically smaller than conventional ovens, making them ideal for small kitchens or apartments.
Cons/Limitations:
1. **Uneven Heating:** Microwaves can sometimes heat food unevenly, particularly thick or dense items.
2. **Limited Browning:** Microwaves do not typically brown food as effectively as conventional ovens.
3. **Texture Changes:** Microwaving can sometimes alter the texture of food, making it rubbery or dry.
4. **Not Suitable for All Cooking Tasks:** Microwaves are not ideal for all cooking tasks, such as baking delicate pastries or roasting large cuts of meat.
Ideal User Profile
Microwave ovens are best suited for individuals and families who value speed, convenience, and ease of use. They are particularly useful for reheating leftovers, cooking simple meals, and defrosting food. Microwave ovens with advanced features, such as convection cooking and grilling, are ideal for users who want to expand their cooking capabilities.
Key Alternatives
1. **Conventional Ovens:** Conventional ovens offer more even heating and browning capabilities, but they are less energy-efficient and take longer to cook food.
2. **Toaster Ovens:** Toaster ovens are smaller and more energy-efficient than conventional ovens, but they offer limited cooking capacity.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Microwave ovens are an indispensable appliance in modern kitchens, offering unparalleled speed, convenience, and ease of use. While they have some limitations, their benefits far outweigh their drawbacks. We recommend choosing a microwave oven with features that align with your specific cooking needs and preferences. Models with inverter technology, sensor cooking, and convection cooking offer the best overall performance. Acknowledging that brands often have affiliations, it’s always best to compare models across different manufacturers to find the best fit.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and answers related to microwave use, addressing common user concerns and advanced queries:
1. **Question:** Can I use any type of container in the microwave?
**Answer:** No, it’s crucial to use microwave-safe containers. Glass, ceramic, and certain plastics labeled as microwave-safe are generally acceptable. Avoid using metal containers, as they can cause sparks and damage the microwave. Always check the manufacturer’s instructions before using a container in the microwave.
2. **Question:** Why does my food sometimes have cold spots after microwaving?
**Answer:** Cold spots occur due to uneven microwave distribution. Ensure the food is evenly distributed in the container and stir it halfway through the cooking process. Using a microwave-safe turntable can also help promote more even heating.
3. **Question:** Is it safe to stand directly in front of the microwave while it’s operating?
**Answer:** Modern microwaves are designed with safety features that minimize radiation leakage. However, it’s generally recommended to stand a few feet away from the microwave while it’s operating, especially if you have any concerns about radiation exposure. Maintain the appliance well, and inspect it for damage.
4. **Question:** How can I prevent food from splattering inside the microwave?
**Answer:** Covering the food with a microwave-safe lid or plastic wrap (with vents) can help prevent splattering. Paper towels can also be used to absorb moisture and prevent messes.
5. **Question:** What’s the best way to reheat leftovers in the microwave?
**Answer:** Place leftovers in a microwave-safe container and add a tablespoon or two of water to help retain moisture. Cover the container and microwave in short intervals, stirring occasionally to ensure even heating.
6. **Question:** Can I cook raw meat in the microwave?
**Answer:** While it’s possible to cook raw meat in the microwave, it’s generally not recommended due to the risk of uneven cooking and potential foodborne illness. If you do cook raw meat in the microwave, ensure it reaches a safe internal temperature.
7. **Question:** Why does my microwave sometimes make a loud buzzing noise?
**Answer:** A loud buzzing noise can indicate a problem with the magnetron or other components. It’s best to consult a qualified technician to diagnose and repair the issue. Continuing to use the microwave with a buzzing noise can potentially damage the appliance.
8. **Question:** How often should I clean my microwave?
**Answer:** It’s recommended to clean your microwave regularly, at least once a week, to prevent food buildup and odors. Wipe down the interior with a damp cloth and mild detergent. For stubborn stains, you can microwave a bowl of water with lemon juice or vinegar for a few minutes to loosen the grime.
9. **Question:** What are the benefits of using a microwave with inverter technology?
**Answer:** Inverter technology provides consistent power levels throughout the cooking process, resulting in more even heating and preventing food from becoming rubbery or overcooked. It’s particularly beneficial for defrosting and cooking delicate foods.
10. **Question:** Can I use aluminum foil in the microwave?
**Answer:** Small, smooth pieces of aluminum foil can sometimes be used to shield certain areas of food from overcooking. However, it’s crucial to avoid using large pieces of foil or allowing the foil to touch the sides of the microwave, as this can cause sparks and damage the appliance.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, microwaves are indispensable tools in modern life, offering a wide range of applications beyond simple food reheating. From their core functionality in heating and cooking to their advanced features and diverse applications in various industries, microwaves continue to evolve and shape our world. By understanding the principles behind microwave technology and its various uses, we can appreciate its significance and harness its potential to improve our lives. We’ve aimed to provide an expert and trustworthy guide to the question of “what are microwaves used for”.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided valuable insights into the multifaceted world of microwaves. Now, we encourage you to share your own experiences with microwave technology in the comments below. What are your favorite microwave recipes or tips? What challenges have you encountered while using microwaves? Share your thoughts and contribute to the collective knowledge of microwave enthusiasts. Contact our experts for a consultation on advanced microwave applications.
