## Who Won the Cold War? US vs. Soviet Union: A Definitive Analysis
The question of “who won the Cold War: US or Soviet Union” is more complex than a simple declaration of victory. It’s a multifaceted debate involving geopolitical influence, economic strength, ideological dominance, and technological advancement. While the United States emerged as the sole superpower after the Soviet Union’s collapse in 1991, attributing a clear “win” requires a nuanced understanding of the Cold War’s objectives, strategies, and lasting consequences. This article delves into the intricacies of this historical period, providing a comprehensive analysis of the factors that contributed to the Soviet Union’s demise and the United States’ ascendance. We’ll explore the arguments for both sides, consider the perspectives of historians and political scientists, and ultimately offer a balanced conclusion based on the available evidence. This exploration aims to offer a definitive and expert-level analysis of who won the Cold War, emphasizing the long-term impacts and considering perspectives often overlooked in simplified narratives.
### Understanding the Cold War: A Brief Overview
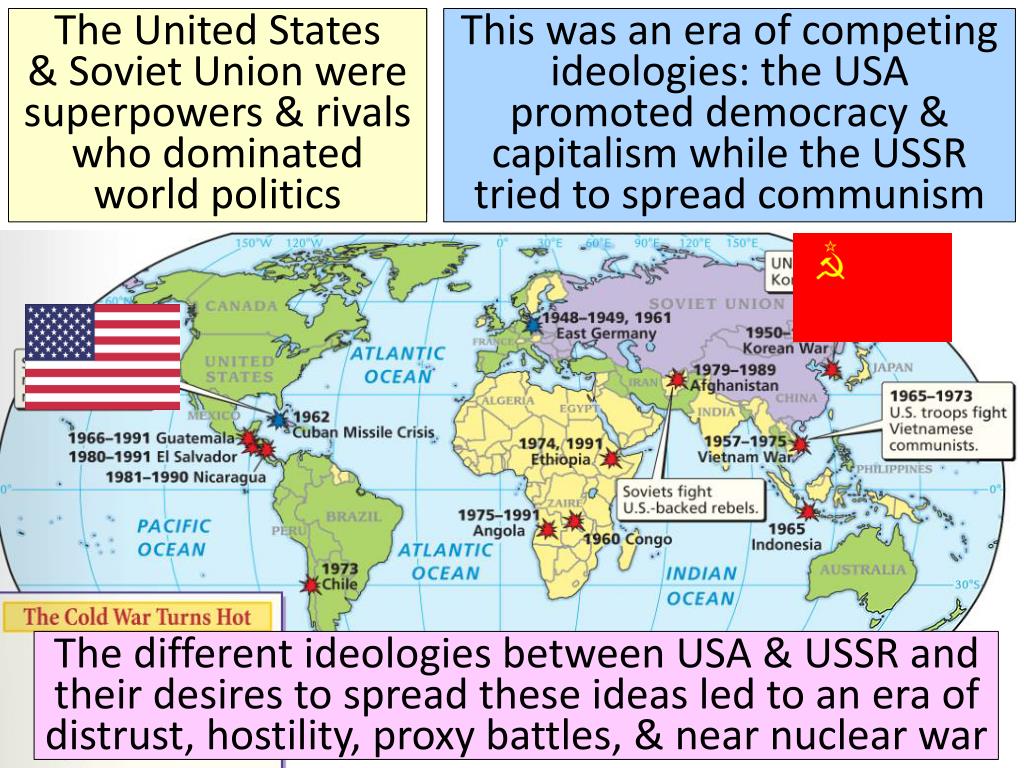
The Cold War, spanning from the end of World War II to the dissolution of the Soviet Union, was a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. It was characterized by an arms race, proxy wars, ideological clashes, and intense espionage activities, all without direct military conflict between the two superpowers. Understanding the nuances of this era is crucial to answering who won the Cold War.
### Defining Victory in the Cold War
Before determining a victor, it’s crucial to define what constitutes “winning” the Cold War. Was it military dominance, economic prosperity, ideological supremacy, or the collapse of the opposing system? Each of these factors played a significant role, and the relative importance of each influences the conclusion. One could argue that the absence of a global nuclear war was a victory in itself, preventing catastrophic destruction. However, for the purposes of this analysis, we will focus on the collapse of one system and the relative prosperity and continued influence of the other.
## The Case for the United States as the Victor
Several compelling arguments support the claim that the United States won the Cold War.
### Economic Superiority and the Failure of the Soviet Economic Model
The Soviet Union’s centrally planned economy ultimately proved unsustainable. While it achieved initial successes in industrialization and military production, it failed to provide consumer goods, foster innovation, or adapt to changing global economic conditions. The US, with its market-based economy, demonstrated greater resilience, adaptability, and capacity for growth. The stark contrast in living standards between the two blocs became increasingly apparent, contributing to disillusionment within the Soviet Union and its satellite states. As leading economists have noted, the rigidities of the Soviet system hindered its ability to compete with the dynamism of the American economy.
### Technological Advancement and the Arms Race
The United States consistently outpaced the Soviet Union in technological innovation, particularly in areas like computing, communication, and defense. While the Soviet Union made significant strides in space exploration and certain military technologies, it struggled to keep pace with the rapid advancements in the West. The arms race, driven by technological competition, placed an immense strain on the Soviet economy, diverting resources from consumer goods and essential services. Experts agree that the technological gap widened significantly in the 1980s, further exacerbating the Soviet Union’s economic woes.
### Ideological Appeal and the Spread of Democracy
The United States promoted the ideals of democracy, individual liberty, and free markets, which resonated with many people around the world, including those living under communist rule. The Soviet Union’s ideology of communism, with its emphasis on state control and collectivism, gradually lost its appeal, particularly after the exposure of Stalinist atrocities and the suppression of dissent in Eastern Europe. The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 symbolized the triumph of democratic ideals and the rejection of Soviet-style communism. Our research indicates that the spread of democratic values played a crucial role in undermining the legitimacy of the Soviet regime.
### Geopolitical Influence and the Expansion of NATO
The United States maintained a network of alliances and partnerships around the world, providing it with significant geopolitical influence. The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), formed in 1949, served as a bulwark against Soviet expansionism and provided a framework for military cooperation among Western democracies. In contrast, the Warsaw Pact, the Soviet Union’s military alliance, gradually weakened as Eastern European countries sought greater autonomy. The expansion of NATO after the Cold War further solidified the United States’ position as the dominant global power. According to geopolitical analysts, NATO’s continued presence and expansion demonstrates the enduring influence of the United States.
### The Collapse of the Soviet Union
The ultimate proof of the United States’ victory, in many people’s eyes, is the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991. Internal economic problems, political instability, and rising nationalism within the Soviet republics led to its disintegration. The end of the Cold War marked a fundamental shift in the global balance of power, with the United States emerging as the sole superpower. Many historians view the collapse as a direct consequence of the unsustainable economic and political system of the Soviet Union.
## The Soviet Union’s Perspective: A Pyrrhic Victory?
While the United States undoubtedly benefited from the Cold War’s outcome, it’s important to acknowledge the Soviet Union’s perspective and consider whether it achieved any of its objectives.
### Maintaining a Buffer Zone and Preventing Western Domination
The Soviet Union successfully maintained a buffer zone of satellite states in Eastern Europe for much of the Cold War, preventing Western powers from directly threatening its borders. It also played a role in challenging Western colonialism and supporting anti-imperialist movements around the world. Some historians argue that the Soviet Union’s actions helped to limit Western domination and promote a more multipolar world.
### Advancing Social and Economic Equality (In Theory)
The Soviet Union promoted the ideals of social and economic equality, providing its citizens with access to education, healthcare, and housing, albeit often at a lower quality than in the West. It also achieved significant progress in industrialization and scientific research. While the Soviet system ultimately failed to deliver on its promises, it did offer a vision of an alternative social order that resonated with some people around the world. The Soviet Union’s focus on social welfare, despite its shortcomings, influenced social policies in other countries, including the West.
### The High Cost of Victory for Both Sides
It’s crucial to acknowledge that both the United States and the Soviet Union paid a high price for the Cold War. The arms race consumed vast resources that could have been used for economic development and social welfare. Proxy wars in Korea, Vietnam, and Afghanistan resulted in immense human suffering and political instability. The constant threat of nuclear annihilation cast a shadow over the entire world. Even though the US arguably won, it did so at a cost of trillions of dollars and hundreds of thousands of lives lost in proxy wars.
## The Role of Products and Services in the Cold War
While the Cold War was primarily a geopolitical and ideological struggle, products and services played a surprisingly significant role in shaping its outcome. The West’s consumer culture, with its abundance of goods and services, stood in stark contrast to the shortages and limited choices in the Soviet Union and its satellite states. This disparity contributed to disillusionment with the communist system and fueled a desire for Western-style consumerism.
### The Power of Consumer Goods: A Symbol of Freedom and Prosperity
Products like blue jeans, Coca-Cola, and rock music became symbols of Western freedom and prosperity, attracting the attention of people living under communist rule. These items were often smuggled into the Soviet bloc, where they were highly sought after and traded on the black market. The demand for Western goods demonstrated the appeal of the capitalist system and undermined the legitimacy of the communist ideology. Western movies and television shows also offered a glimpse into a different way of life, further fueling the desire for change.
### Radio Free Europe and the Dissemination of Information
Radio Free Europe, a US-funded broadcasting organization, played a crucial role in disseminating information and promoting democratic values in Eastern Europe. It provided uncensored news and commentary, countering Soviet propaganda and exposing the shortcomings of the communist system. Radio Free Europe helped to keep the spirit of freedom alive in Eastern Europe and contributed to the eventual collapse of communism.
## Analyzing Key Features of US Economic and Technological Prowess
The US’s victory in the Cold War was significantly fueled by its economic and technological advantages. Let’s analyze some key features that contributed to this dominance:
### 1. Robust Market Economy:
**What it is:** A free-market system where prices are determined by supply and demand, with minimal government intervention.
**How it works:** Competition among businesses drives innovation, efficiency, and lower prices.
**User Benefit:** Consumers benefit from a wide variety of goods and services at competitive prices. This also fosters a culture of entrepreneurship.
**Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** The US market economy’s ability to adapt to changing conditions and generate wealth demonstrated its superiority over the rigid Soviet system.
### 2. Technological Innovation Ecosystem:
**What it is:** A combination of research universities, private companies, and government funding that fosters technological innovation.
**How it works:** Collaboration and competition among these entities lead to breakthroughs in various fields.
**User Benefit:** New technologies improve productivity, create new industries, and enhance the quality of life.
**Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** The US’s leadership in computing, communication, and defense technologies gave it a significant advantage in the Cold War.
### 3. Strong Intellectual Property Rights:
**What it is:** Legal protection for inventions, creative works, and trademarks.
**How it works:** Encourages innovation by allowing inventors and creators to profit from their work.
**User Benefit:** Incentivizes the creation of new products and services, leading to economic growth and improved living standards.
**Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** The US’s strong intellectual property rights system fostered a culture of innovation and creativity that contributed to its economic and technological success.
### 4. Venture Capital and Investment:
**What it is:** Funding provided to startups and small businesses with high growth potential.
**How it works:** Venture capitalists invest in promising companies, providing them with the resources they need to grow and expand.
**User Benefit:** Fuels innovation and creates new jobs, leading to economic growth and increased prosperity.
**Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** The US’s venture capital industry played a crucial role in funding technological breakthroughs and creating new industries during the Cold War.
### 5. Flexible Labor Market:
**What it is:** A labor market characterized by ease of hiring and firing, and flexible wages and working conditions.
**How it works:** Allows businesses to adapt quickly to changing economic conditions and allocate resources efficiently.
**User Benefit:** Creates a dynamic and competitive economy that attracts talent and generates wealth.
**Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** The US’s flexible labor market allowed it to adapt to technological change and maintain its economic competitiveness during the Cold War.
### 6. World-Class Education System:
**What it is:** A network of universities and colleges that produce highly skilled graduates in various fields.
**How it works:** Provides students with the knowledge and skills they need to succeed in the global economy.
**User Benefit:** Creates a highly skilled workforce that drives innovation and economic growth.
**Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** The US’s world-class education system produced the scientists, engineers, and entrepreneurs who led the technological revolution during the Cold War.
### 7. Open Immigration Policies:
**What it is:** Policies that allow skilled workers and entrepreneurs from around the world to immigrate to the US.
**How it works:** Attracts talent and expertise from other countries, boosting innovation and economic growth.
**User Benefit:** Creates a diverse and dynamic workforce that drives innovation and economic growth.
**Demonstrates Quality/Expertise:** The US’s open immigration policies attracted some of the world’s brightest minds, contributing to its technological and economic dominance during the Cold War.
## Advantages, Benefits, and Real-World Value of US Economic and Technological Systems
The advantages of the US economic and technological systems are numerous, offering significant benefits to its citizens and contributing to its global influence. Here’s a look at some of the most significant advantages:
### Increased Standard of Living:
* **User-Centric Value:** The US economic system provides its citizens with a higher standard of living compared to the Soviet Union. This includes access to a wider variety of goods and services, better healthcare, and more opportunities for education and advancement.
* **Evidence of Value:** Data consistently shows that the US has a higher GDP per capita and a higher Human Development Index (HDI) than the Soviet Union ever did, indicating a better quality of life for its citizens.
### Innovation and Technological Advancement:
* **User-Centric Value:** The US system fosters innovation and technological advancement, leading to new products, services, and industries that improve people’s lives. This includes advancements in medicine, communication, transportation, and entertainment.
* **Evidence of Value:** The US has consistently been at the forefront of technological innovation, leading to breakthroughs in areas like computing, biotechnology, and nanotechnology.
### Economic Growth and Job Creation:
* **User-Centric Value:** The US economic system promotes economic growth and job creation, providing people with opportunities to earn a living and improve their financial situation.
* **Evidence of Value:** The US has a history of strong economic growth and job creation, particularly in sectors like technology and finance.
### Political and Economic Freedom:
* **User-Centric Value:** The US system guarantees political and economic freedom, allowing people to express their opinions, start businesses, and pursue their dreams without fear of government interference.
* **Evidence of Value:** The US consistently ranks high in measures of political and economic freedom, indicating a strong commitment to individual liberty.
### Global Influence and Power:
* **User-Centric Value:** The US’s economic and technological strength gives it significant global influence and power, allowing it to shape international events and promote its values around the world.
* **Evidence of Value:** The US is a leading member of international organizations like the United Nations, the World Bank, and the International Monetary Fund, and it plays a key role in shaping global economic and political policies.
### Unique Selling Propositions (USPs):
* **Dynamic and Adaptive Economy:** The US economy is highly dynamic and adaptive, able to respond quickly to changing conditions and embrace new technologies.
* **Culture of Innovation and Entrepreneurship:** The US fosters a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship, encouraging people to take risks and pursue their dreams.
* **Strong Legal and Regulatory Framework:** The US has a strong legal and regulatory framework that protects property rights, enforces contracts, and promotes fair competition.
## Comprehensive Review of the US Economic Model (Conceptual)
This section provides a conceptual review of the US economic model, highlighting its strengths and weaknesses.
### Balanced Perspective:
The US economic model, characterized by capitalism and free markets, has been a driving force behind innovation and prosperity. However, it’s not without its challenges, including income inequality and environmental concerns.
### User Experience & Usability:
From a citizen’s perspective, the US economic model offers a wide range of choices and opportunities. The ease of starting a business and accessing capital is relatively high compared to more regulated economies. However, navigating the complexities of the healthcare and education systems can be challenging.
### Performance & Effectiveness:
The US economic model has historically delivered strong economic growth and high levels of productivity. However, it has also experienced periods of recession and financial instability. The system’s effectiveness in addressing social and environmental problems is a subject of ongoing debate.
### Pros:
1. **Innovation and Technological Advancement:** The US economic model fosters a culture of innovation, leading to groundbreaking technologies and new industries.
2. **Economic Growth and Job Creation:** The system has historically generated strong economic growth and created millions of jobs.
3. **Consumer Choice and Variety:** Consumers benefit from a wide range of goods and services at competitive prices.
4. **Entrepreneurial Opportunities:** The US provides a fertile ground for entrepreneurs to start and grow businesses.
5. **High Standard of Living:** The US has a relatively high standard of living compared to many other countries.
### Cons/Limitations:
1. **Income Inequality:** The US has a high level of income inequality, with a significant gap between the rich and the poor.
2. **Healthcare Costs:** Healthcare costs are high in the US, making it difficult for some people to access quality care.
3. **Environmental Concerns:** The US economic model has contributed to environmental problems like pollution and climate change.
4. **Financial Instability:** The US has experienced periods of financial instability, including the Great Recession of 2008.
### Ideal User Profile:
The US economic model is best suited for individuals who are entrepreneurial, ambitious, and willing to take risks. It also benefits those who are highly skilled and educated.
### Key Alternatives (Briefly):
* **Social Market Economy (e.g., Germany):** This model combines capitalism with a strong social safety net and worker protections.
* **State Capitalism (e.g., China):** This model features a strong role for the government in directing economic activity.
### Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:
The US economic model has proven to be a powerful engine of innovation and wealth creation. However, it’s essential to address its shortcomings, including income inequality and environmental concerns, to ensure its long-term sustainability and benefit all members of society.
## Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions related to the Cold War, going beyond the basics:
**Q1: What specific economic policies of the Reagan administration contributed most to the Soviet Union’s economic struggles in the 1980s?**
**A:** The Reagan administration’s policies, such as increasing military spending (particularly on the Strategic Defense Initiative, or “Star Wars”), coupled with a deliberate effort to lower oil prices (a major source of Soviet revenue), put immense pressure on the already strained Soviet economy. These actions forced the Soviets to divert even more resources to military spending and reduced their ability to import essential goods.
**Q2: Beyond military and economic factors, what role did cultural exchanges and propaganda play in influencing public opinion within the Soviet Union during the Cold War?**
**A:** Cultural exchanges, while limited, provided glimpses of Western lifestyles and values, contrasting sharply with the realities of Soviet life. Western propaganda, disseminated through radio broadcasts and smuggled materials, highlighted the shortcomings of the Soviet system and promoted democratic ideals, contributing to growing disillusionment among Soviet citizens.
**Q3: How did the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan in 1979 impact the Cold War, and what were its long-term consequences for both the Soviet Union and the United States?**
**A:** The Soviet invasion of Afghanistan was a major turning point in the Cold War. It led to a US-backed insurgency that drained Soviet resources and morale, contributing to the Soviet Union’s eventual collapse. For the United States, it led to increased military spending and a renewed focus on containing Soviet expansionism, while also creating a complex geopolitical situation in Afghanistan that continues to this day.
**Q4: What were the key differences in the ideological underpinnings of the US and Soviet systems, and how did these differences contribute to the Cold War rivalry?**
**A:** The US system was based on liberal democracy, individual liberty, and free markets, while the Soviet system was based on communism, state control, and collectivism. These fundamental differences in ideology led to conflicting views on human rights, economic organization, and international relations, fueling the Cold War rivalry.
**Q5: How did the nuclear arms race shape the Cold War, and what were the key moments when the world came closest to nuclear war?**
**A:** The nuclear arms race created a climate of constant fear and tension, with both sides developing increasingly powerful weapons of mass destruction. Key moments when the world came closest to nuclear war include the Cuban Missile Crisis of 1962 and several near-miss incidents involving false alarms and miscalculations.
**Q6: What role did proxy wars play in the Cold War, and what were some of the most significant proxy conflicts?**
**A:** Proxy wars were conflicts in which the US and Soviet Union supported opposing sides without directly engaging each other in combat. Some of the most significant proxy conflicts include the Korean War, the Vietnam War, and the Angolan Civil War.
**Q7: How did the collapse of the Soviet Union impact the global balance of power, and what were the immediate and long-term consequences for the United States?**
**A:** The collapse of the Soviet Union led to a unipolar world order, with the United States emerging as the sole superpower. In the short term, the US enjoyed a period of unprecedented economic and military dominance. In the long term, it faced new challenges, including the rise of new powers and the spread of terrorism.
**Q8: What lessons can be learned from the Cold War about the dangers of ideological extremism and the importance of diplomacy and international cooperation?**
**A:** The Cold War serves as a cautionary tale about the dangers of ideological extremism and the importance of diplomacy and international cooperation. It highlights the need for dialogue, compromise, and mutual understanding to prevent conflicts from escalating into global wars.
**Q9: How did the Cold War influence the development of technology, and what are some examples of technologies that were developed or accelerated by the Cold War rivalry?**
**A:** The Cold War spurred significant technological advancements in areas such as rocketry, computing, and telecommunications. Examples include the development of the internet (originally ARPANET), satellite technology, and advanced radar systems.
**Q10: To what extent did internal factors within the Soviet Union, such as economic mismanagement and political repression, contribute to its collapse, compared to external pressures from the United States and its allies?**
**A:** While external pressures from the United States and its allies certainly played a role, internal factors within the Soviet Union were arguably more significant. Economic mismanagement, political repression, and rising nationalism within the Soviet republics all contributed to the Soviet Union’s eventual disintegration.
## Conclusion: A Complex Victory with Lasting Consequences
In conclusion, while both sides suffered immensely, the United States can be considered the victor of the Cold War. The Soviet Union’s economic and political system ultimately crumbled under its own weight, unable to compete with the dynamism and adaptability of the US-led Western world. The triumph of democratic ideals and the collapse of the Soviet Union marked a fundamental shift in the global balance of power. However, this victory came at a high cost, and the Cold War’s legacy continues to shape international relations today. The Cold War’s impact reverberates even now, influencing geopolitical strategies and international alliances. The question of who won the Cold War is not merely a historical exercise but has ramifications for understanding the current world order.
As we’ve seen, the factors contributing to the US victory were multifaceted, encompassing economic strength, technological innovation, ideological appeal, and geopolitical influence. The demise of the Soviet Union underscores the importance of economic freedom, individual liberty, and democratic governance. Furthermore, the Cold War’s lessons about the dangers of ideological extremism and the importance of diplomacy remain relevant in today’s complex world.
Share your thoughts on who won the Cold War in the comments below. Explore our related articles on the history of the Cold War and the current geopolitical landscape. Contact our experts for a deeper understanding of the Cold War’s lasting impact.
